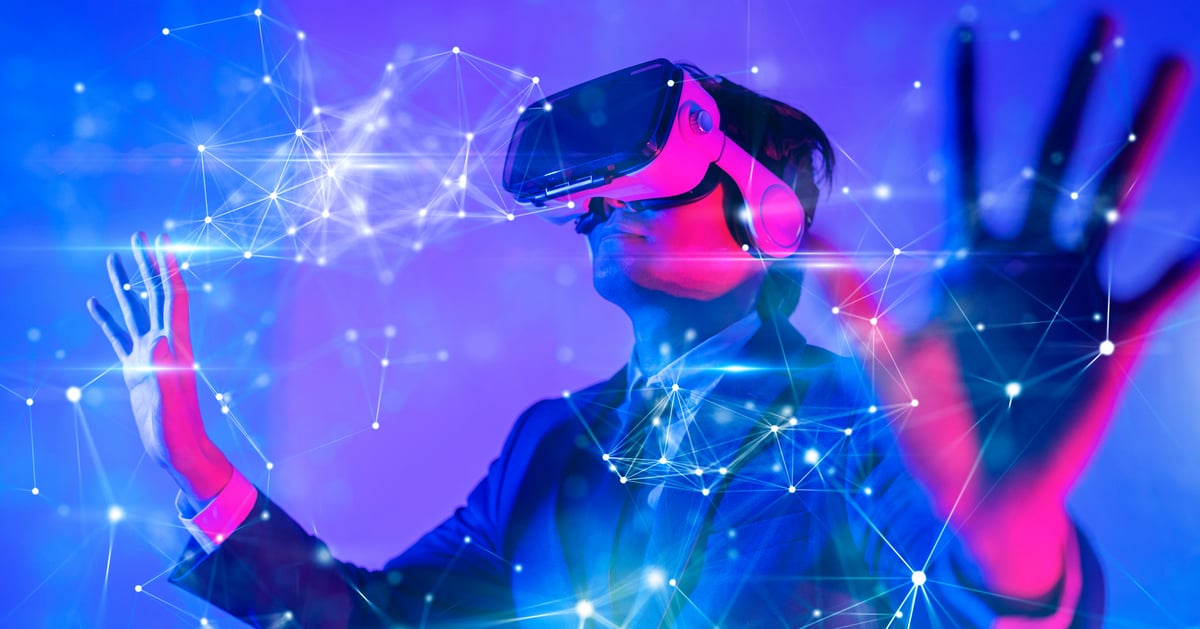
The Metaverse: A world of opportunity
When Gartner cites the metaverse as one of its top strategic technology trends for 2023, the technology has to be taken seriously.
Indeed, according to forecasters, it looks like big business for players in the metaverse industry. Strategic Market Research, for example, puts the value of the metaverse market at $47.48 million in 2022, with a forecast rise to $678 million by 2030. Citi Global Perspectives & Solutions sees potential growth as even bigger, with the total addressable market for the metaverse economy growing to between $8 trillion and $13 trillion by 2030, with some 5 billion users worldwide.
Other commentators are attempting to put numbers on just how ready businesses are for the metaverse. Ciena, for example, reports that 71 of professionals can see the metaverse becoming part of their existing work practices. At the same time, 40 percent believe that collaboration will move away from traditional environments to more immersive and virtual platforms in the next two years.
These are impressive figures, but for many the questions remain – what is this thing called the metaverse, and why is there so much hype around it?
What is the metaverse?
Defining the metaverse is a useful starting point but pinning that down can be as challenging as forecasting the market's growth. The term is not new; it was first mentioned in the 1992 science fiction novel Snow Crash by Neal Stephenson.
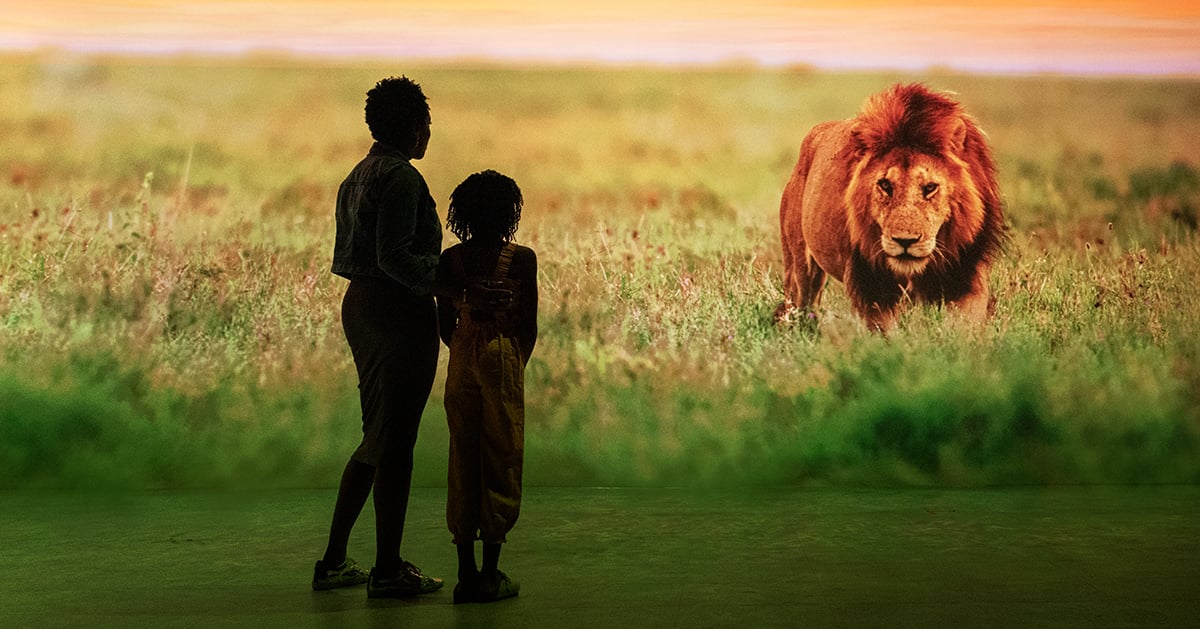
Strategic Market Research puts the definition in application-led terms – a virtual space developed by the fusion of virtually enhanced digital and physical reality with a wide range of practical metaverse applications, such as gaming, healthcare, manufacturing, training and entertainment.
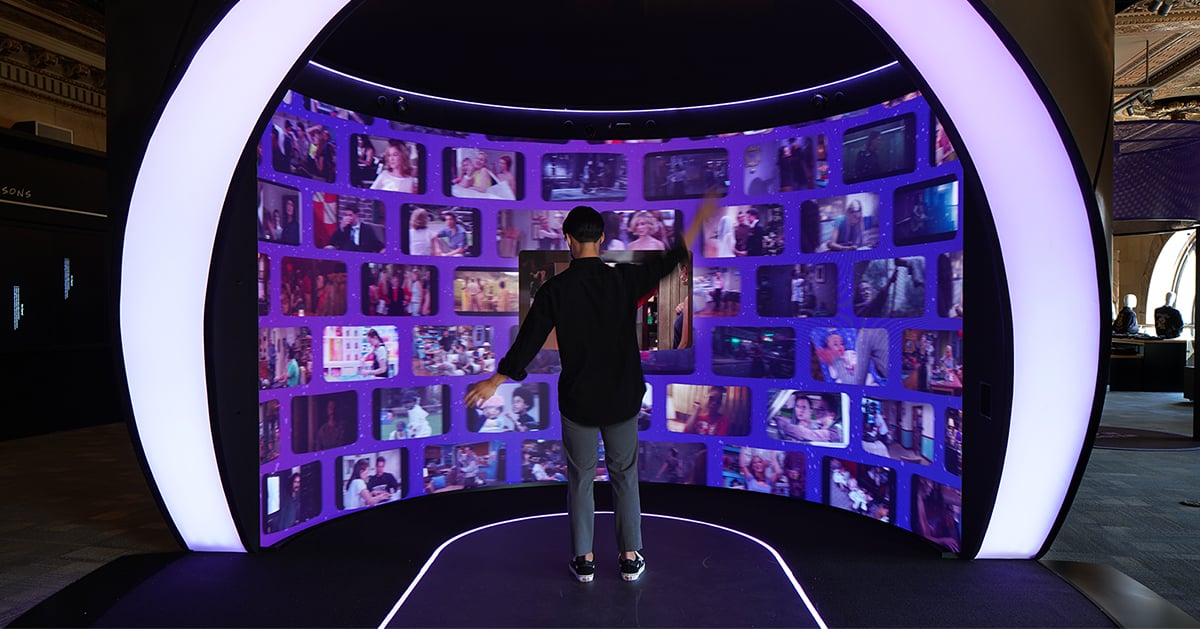
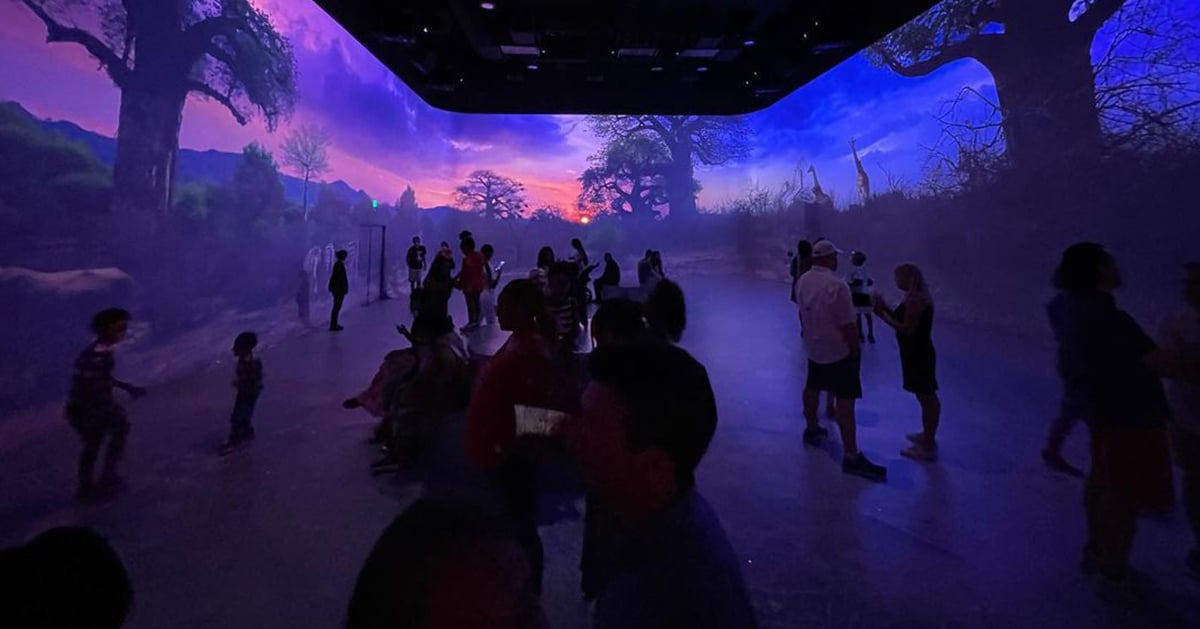
Other commentators see the metaverse as WEB3, the next iteration of the Internet, and social technologies where the physical and digital worlds come together, allowing avatars - digital representations of people – to interact in various virtual environments. The metaverse provides a space for interconnected virtual communities to interact with Technology Platforms enabling engagement such as virtual reality headsets, augmented reality glasses or smartphone apps.
Furthermore we have open and closed metaverses - competing visions without the consensus of an industry standard. Open metaverse is an open-source virtual world platform that supports creating, hosting and exploring virtual worlds and spaces. It provides a flexible and extensible framework for developers to create, customize and deploy their virtual worlds and spaces. A closed metaverse is a digital world that is only accessible to a specific group of people, usually created by a company or organization for internal use and not open to the general public, often used for training, simulations and other business purposes.

Metaverse realities
We are still in the early days of experiencing the metaverse - computing power, headsets, software protocols and human to machine and visa versa interfaces, and networking capacity are just not ready to support a truly immersive and shared metaverse. However, the seeds of the metaverse exist as isolated experiences where assets and value are not interoperable or interchangeable.
Many companies are involved in the metaverse evolution or have significantly invested in ambitious projects with varying degrees of success. Meta (formerly Facebook) has recently scaled down investments while Apple's recent announcement of Vision Pro, a cutting-edge mixed-reality headset introduced to revolutionize virtual and augmented reality could move us closer to the metaverse as they embrace spatial computing.
In the future, a landscape of virtual spaces with transferable identities and assets by blockchains that are interoperable or interchangeable will manifest the metaverse's transactional and identity needs. Whether or not this vision ever arrives enough components of the metaverse already exist to offer opportunities.
Building on existing technologies
The technologies that enable the metaverse are familiar; the way they come together makes current and future iterations of the metaverse possible.
The metaverse combines technology platforms and services, including augmented reality, virtual reality, mixed reality, extended reality, video mapping, virtual production and spatial audio and computing technologies, touch and gesture user interfaces and multisensory and polysensory technologies. Other relevant services and enabling technologies include blockchain, NFTs (non-fungible tokens), content production and photorealistic model forming.
Metaverse business opportunities
The availability of these technologies is already powering several practical and beneficial applications for businesses and consumers.
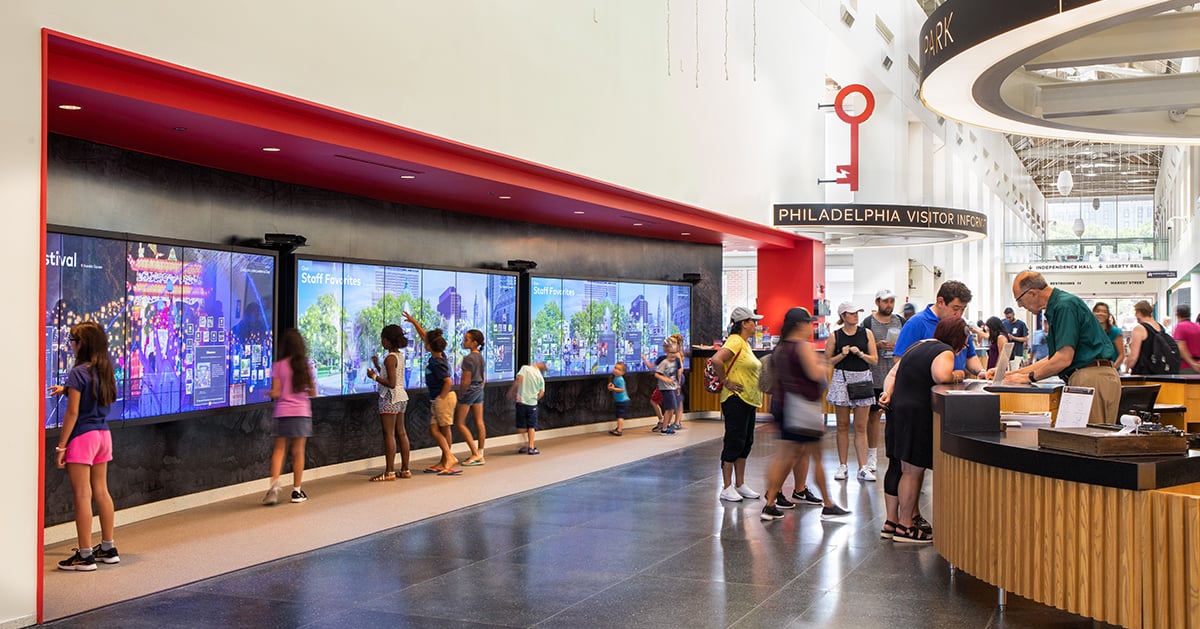
Gaming is currently the largest sector of the market, taking a 51 percent share in 2022, according to Strategic Market Research, with manufacturing at 22 percent. There is growing adoption in other consumer applications such as entertainment, events, retail, experiences and social interaction.
There are also promising applications in training, collaboration, design and development and manufacturing operations in business.
- Virtual collaboration enables teams to meet in virtual workspaces that resemble real offices, interacting face-to-face using digital real-time animated avatars. Experience indicates that it has improved the quality of collaboration, making it an attractive alternative to videoconferencing for businesses with dispersed teams. According to a Ciena survey, 96 percent of respondents saw the value of virtual meetings in improved collaboration.
- Manufacturing processes incorporate metaverse technologies such as augmented and virtual reality to speed up and optimize production line operations.
- Employee training can be improved by using metaverse technologies. Virtual reality experiences, for example, can create an active learning environment, enhancing training outcomes compared with passive learning. Virtual reality can also provide a safer environment for training employees working in hazardous activities or with dangerous materials.
- Design and development processes can benefit from metaverse technologies by allowing designers to create products that never existed in the physical world but can be simulated in digital spaces. Designers can also test responses to new innovative designs in the metaverse before committing development resources, and they can collaborate more efficiently with specialists in virtual meeting spaces.
Samsung, for example, has created a virtual experience to showcase its products and technology, Hyundai's 'Mobility Adventure' allows guests to drive virtual vehicles and air mobility transport and retailer Selfridges collaborated with designers and storytellers to create 'Electric/City', an immersive space where visitors can explore stores and purchase physical or digital garments.

Preparing for the future metaverse
The applications outlined above highlight the potential benefits for metaverse business opportunities and many leading brands are already building the metaverse into their operations.
The concept of the metaverse is based on technology-enabling platforms, as mentioned earlier, and this is not the first time combining the two extremes of innovation technology, exploitation to discovery, using already established technologies to push the boundaries and starting a new technology evolution. The Internet and the World Wide Web is a prime example of that concept and so are AR/VR/MR/XR, Blockchain, NFTs and Massive Multiplayer Online Games (MMOs).
Metaverse represents a complex and multifaceted concept, where no current single technology platform can fully realize its full vision and potential. The audiovisual industry history is full of milestones that have challenged a specific technology adaptation and deployment. No wonder, a wise metaverse specialist interviewed by Forbes suggests starting small and thinking big. It feels like it was only yesterday when we were arguing whether HDTV will work and today many only stream digital media.
Let's perhaps start a small project testing it frequently and see if business opportunities provide tangible benefits!
Ready player one?
Yiannis Cabolis
Yiannis Cabolis, Director of Technology Innovation at Electrosonic, shares the inside track on how technology drives innovation. He brings 30 years’ experience monitoring emerging technologies, developing best practices and driving Research and Development to solve challenges and help clients understand how to benefit from the latest engineered technology solutions.










.jpg?width=1500&height=995&name=ELC501_N17_medium%20(1).jpg)


![[QUIZ - Elevate your next project with our Technology Readiness Assessment]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/5104351/4a658ded-d97c-4f55-a12b-12ca16db609c.png)

.jpg?width=1940&height=500&name=ES_BlogBanner_How%20Ready%20is%20your%20technology%20project%20(1).jpg)