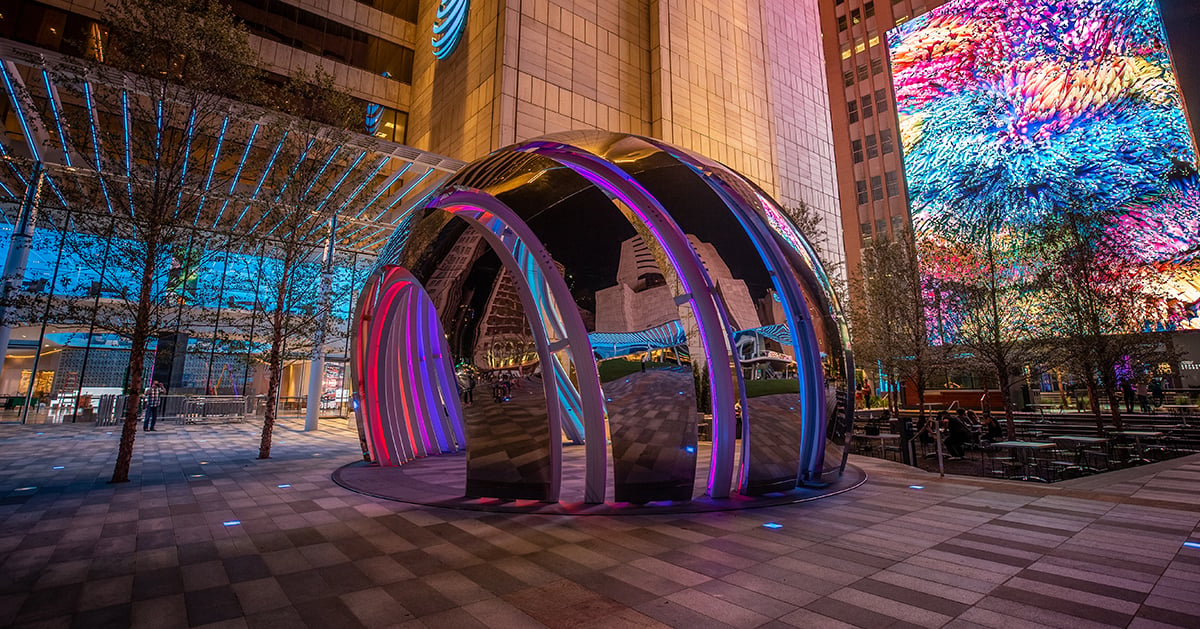
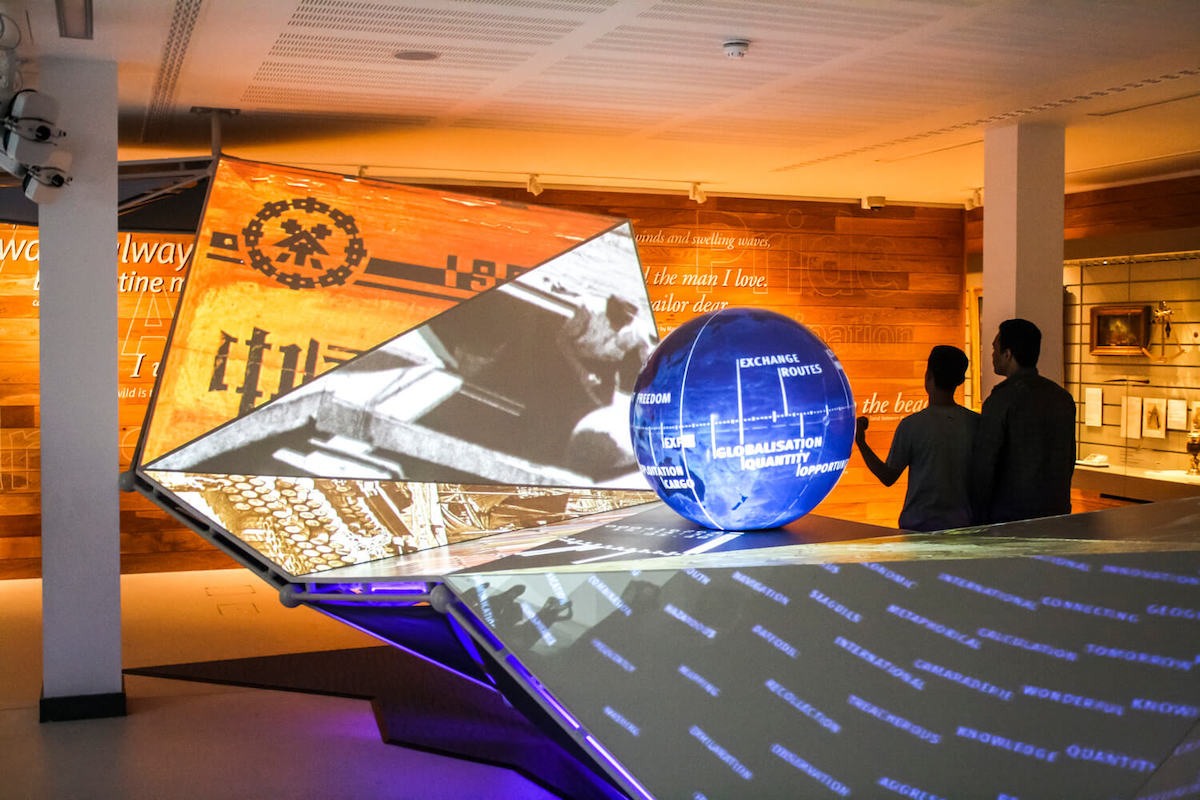
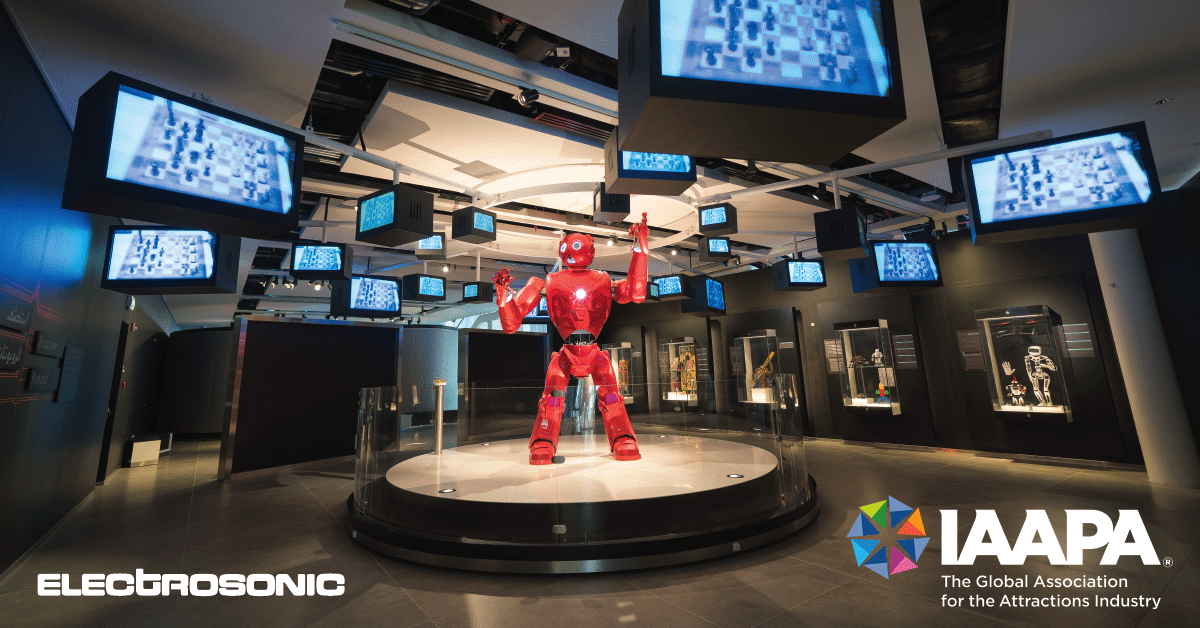
Motion sensing technology: Enhancing the guest experience
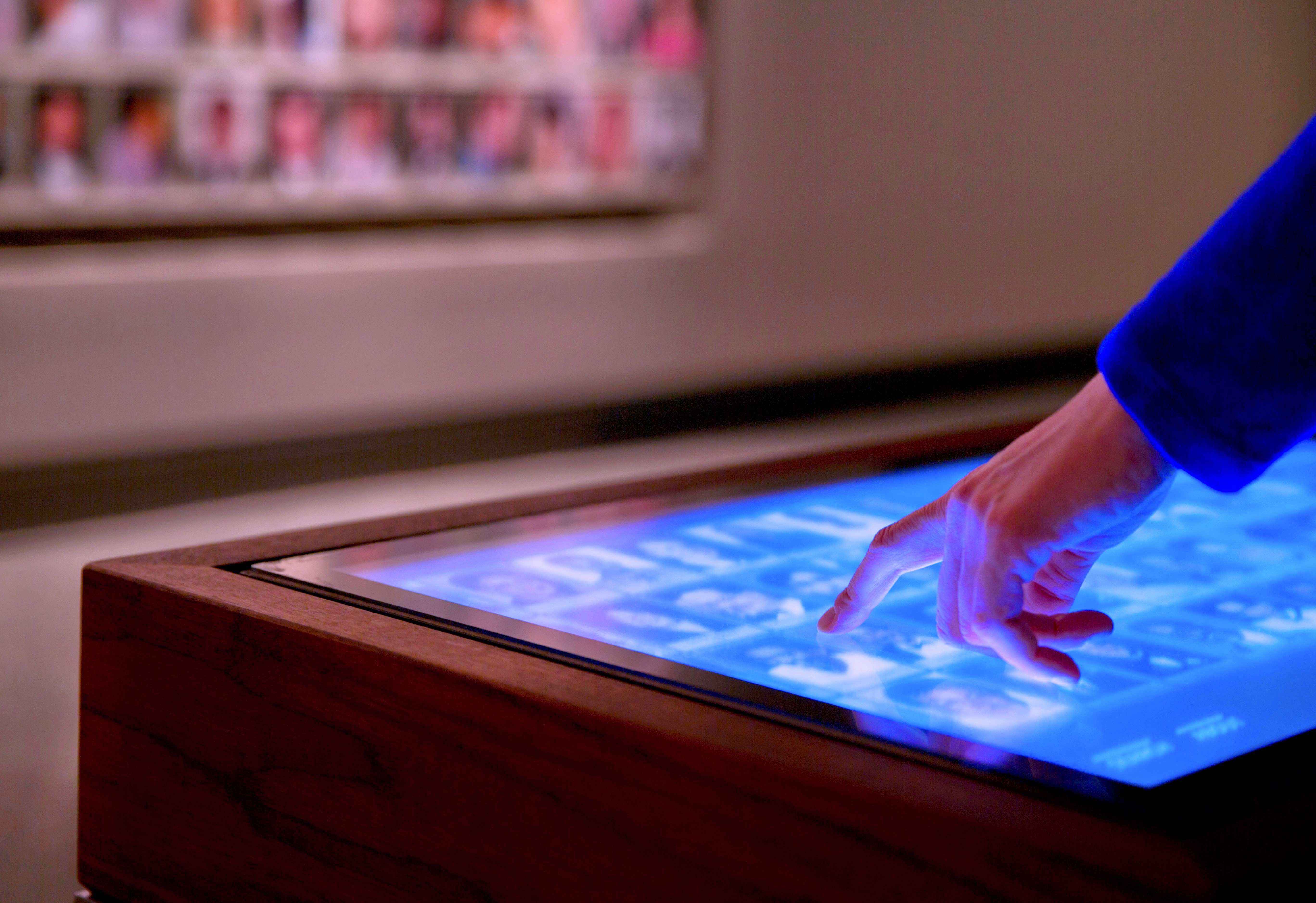
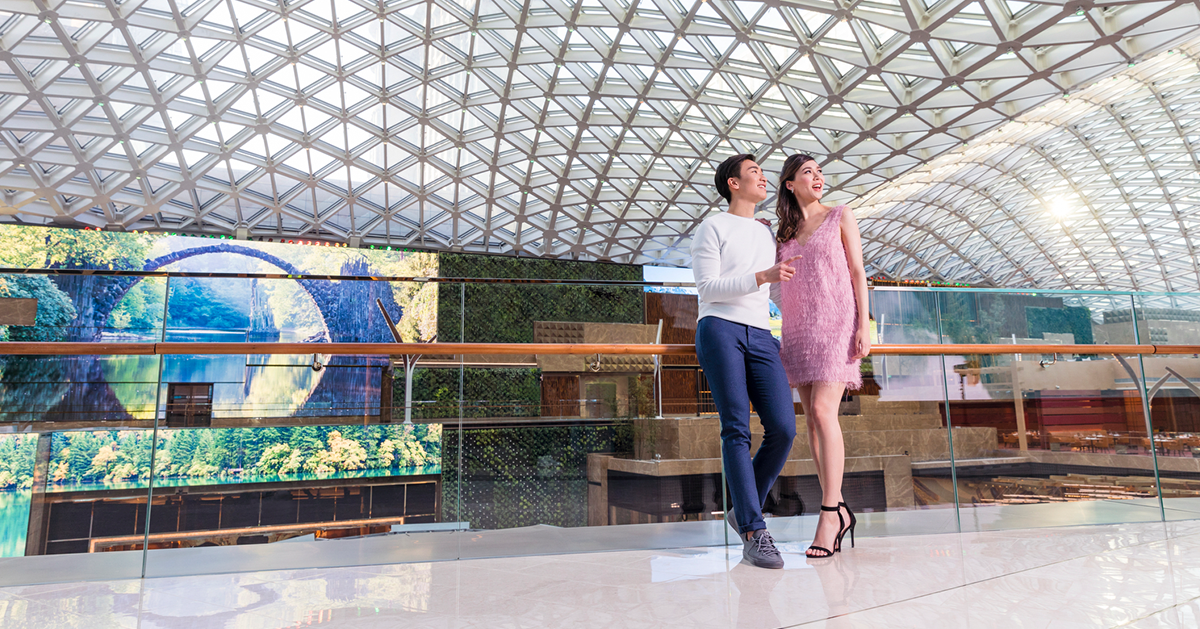
From museums to transportation hubs, retail outlets to commercial buildings, advanced motion sensing technology is revolutionizing interactive experiences in various spaces and destinations.
Motion sensor technology can transform the guest experience, help operators attract more visitors and improve efficiency.
How motion technologies enhance the guest experience
Motion sensor technology has long been integral to physical security monitoring systems. When a surveillance or monitoring system detects motion, it notifies security teams so they can investigate and respond.
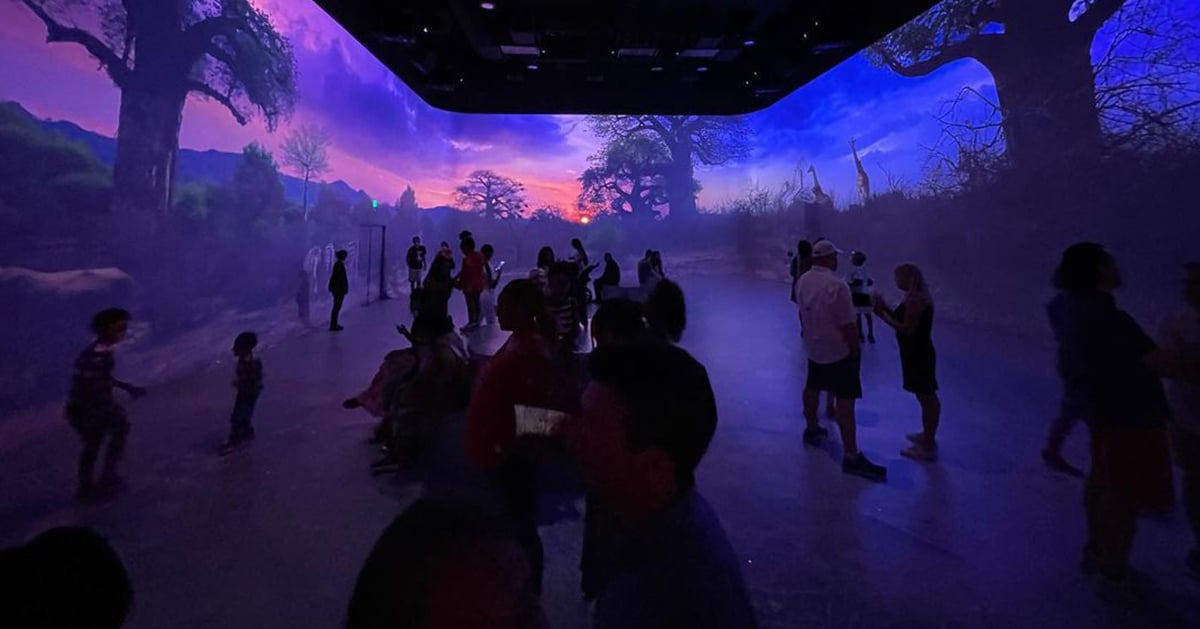
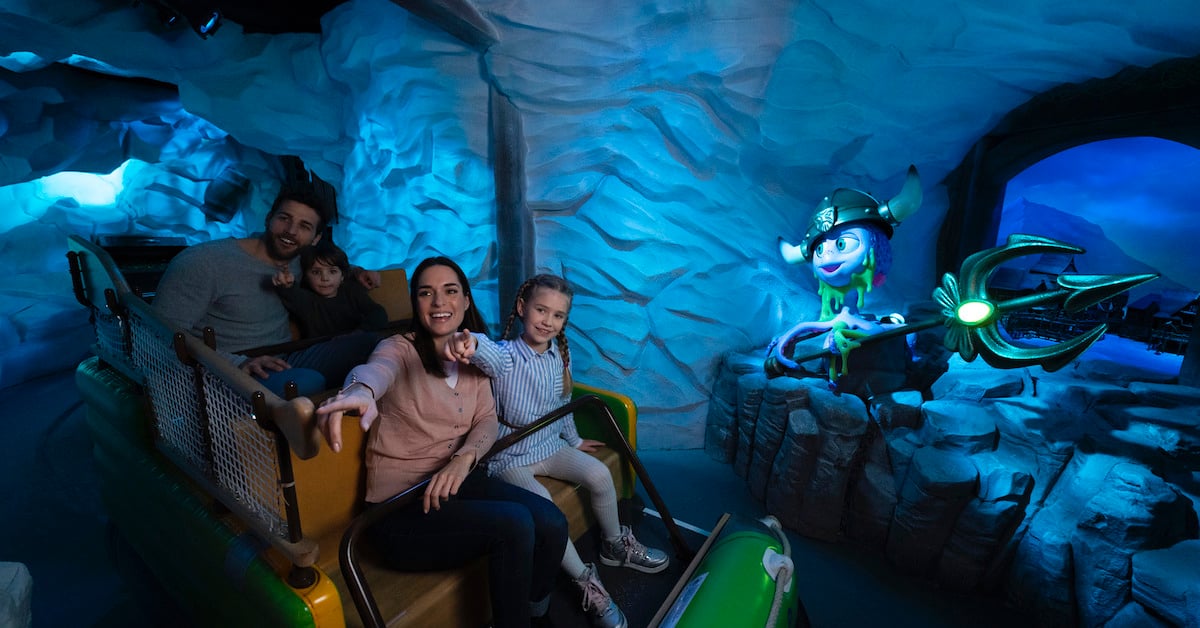
Advanced motion sensors are now widely used in themed and location-based entertainment to enhance guest experience. Interactive motion technologies can trigger dynamic responses in audiovisual systems or creative content, opening exciting new opportunities for interactivity.
Technology designers are creating innovative interactive experiences that respond to movement to entertain or inform guests in compelling ways. Imagine an experience where guests can interact with clips of their favorite TV characters and stories through facial movement, when guests turn the pages of a 'digital book', content changes dynamically. In a busy city center, visitors trigger silhouettes waving and dancing in a window as they approach a building.
Advanced motion sensing technology like that is transforming the guest experience in museums, visitor centers, transportation hubs, retail outlets, commercial buildings and other destinations. However, the scope of guest experience is not limited to entertainment. Advanced motion sensor technology also influences other aspects of the overall guest experience, such as:
- Comfort: Motion technologies detect when a space is occupied. This triggers changes in lighting, air conditioning, heating and other environmental factors to optimize comfort.
- Safety: In busy venues or spaces, motion technologies detect overcrowding or movement. This helps security teams control numbers to ensure guest safety.
- Personalization: Advanced motion sensing technology enables guests to trigger specific interactions based on their preferences.
- Accessibility: Interactive motion technologies automate tasks and controls, making it easier for users to interact with devices and systems without manual intervention.
Other essential benefits exist for owners and operators. To start with, an engaging experience can attract more visitors. Advanced motion sensor technology can also help owners run operations more efficiently. The technology can help reduce energy costs or provide valuable insights into guest behavior and response.
Interactive motion technologies in action
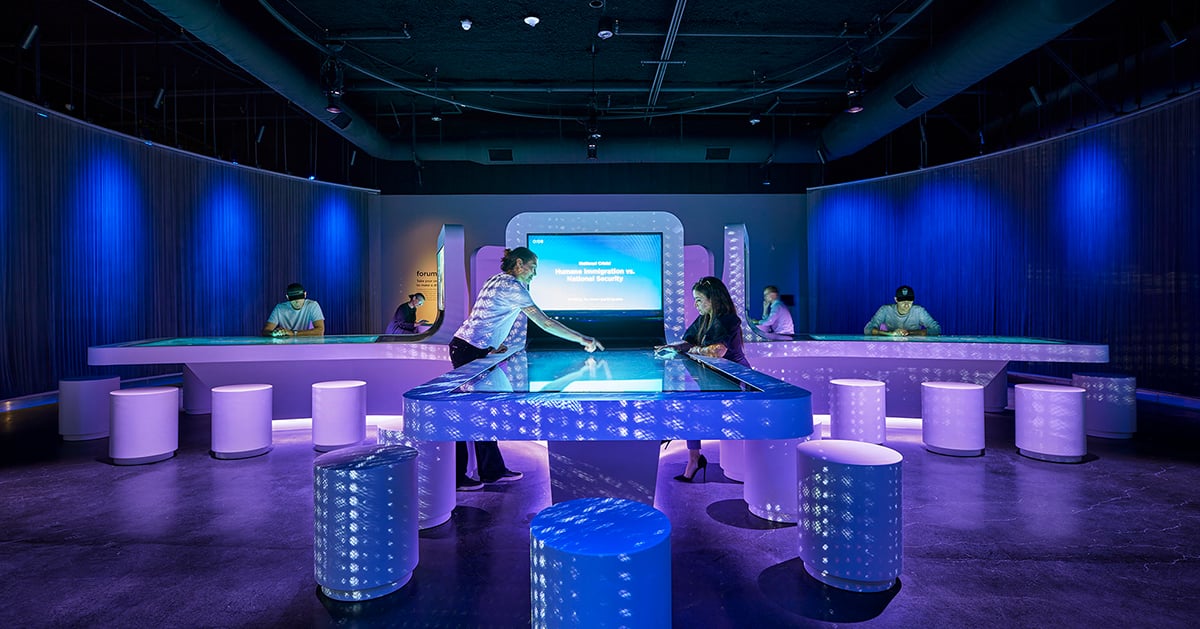
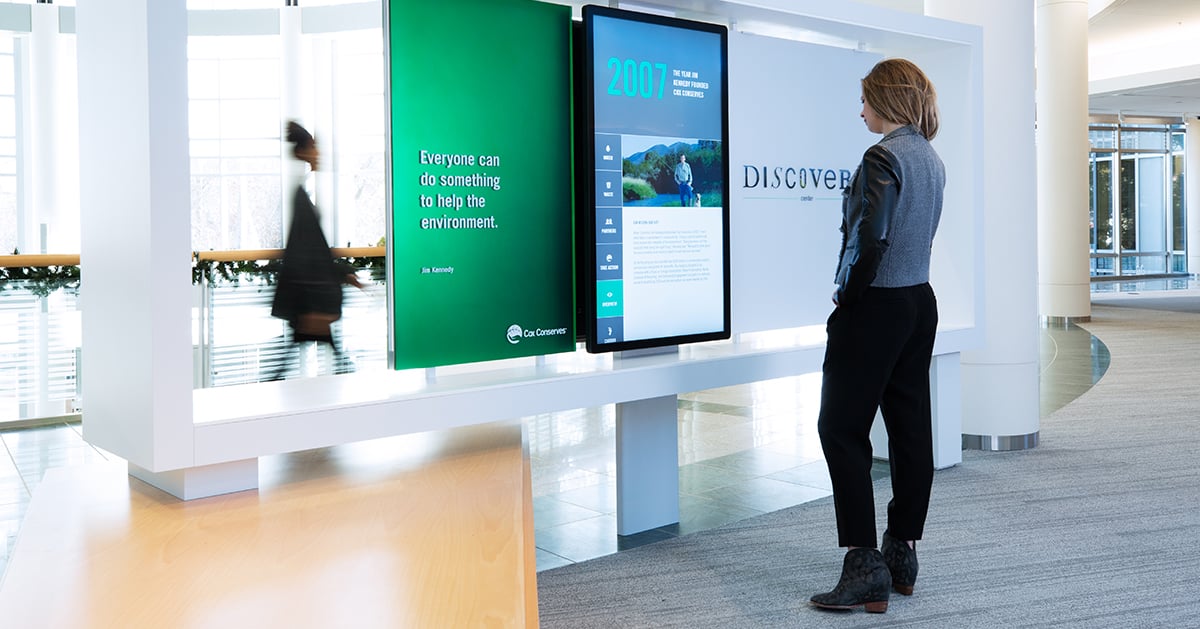
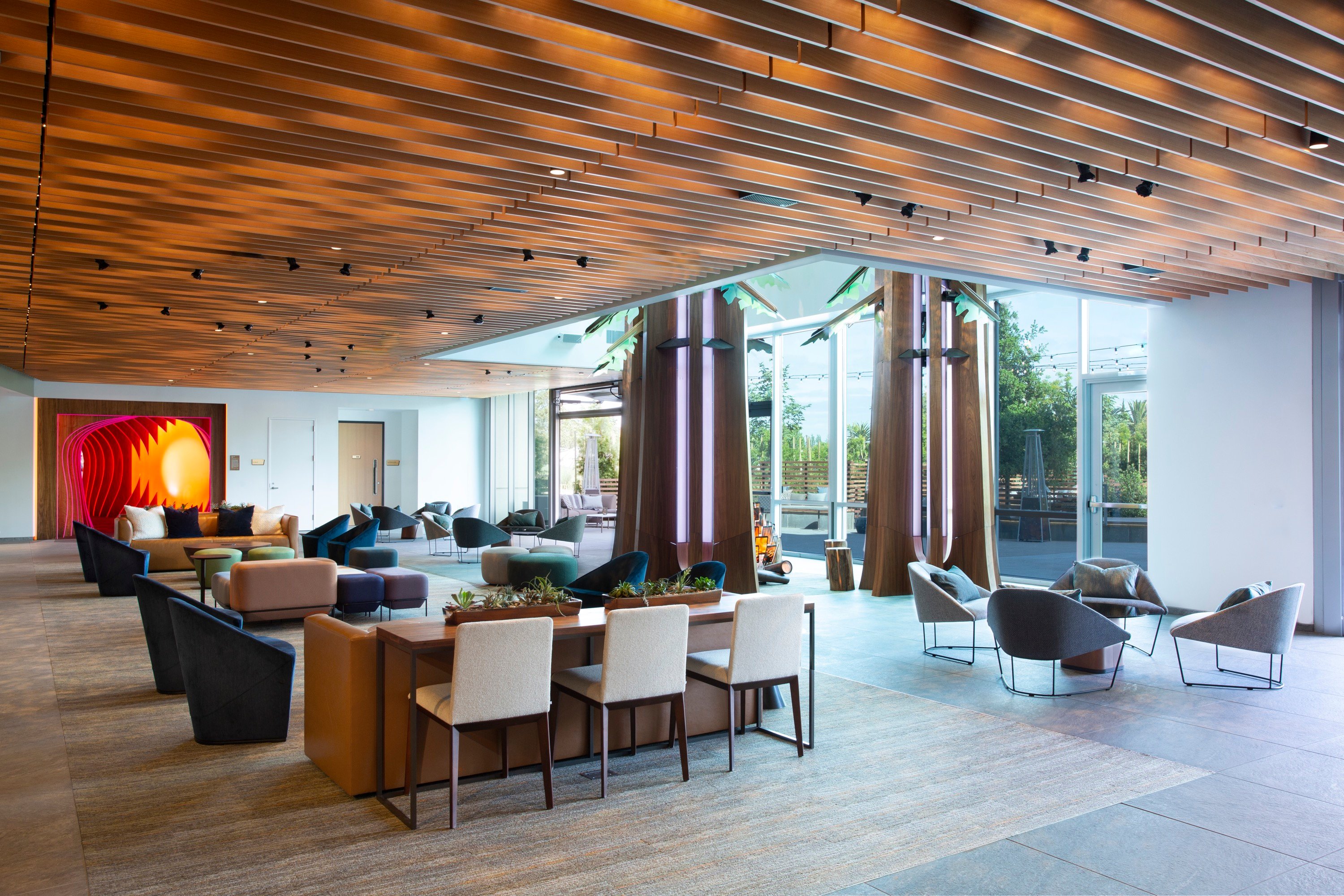
Johnson Controls OpenBlue Innovation Center Milwaukee
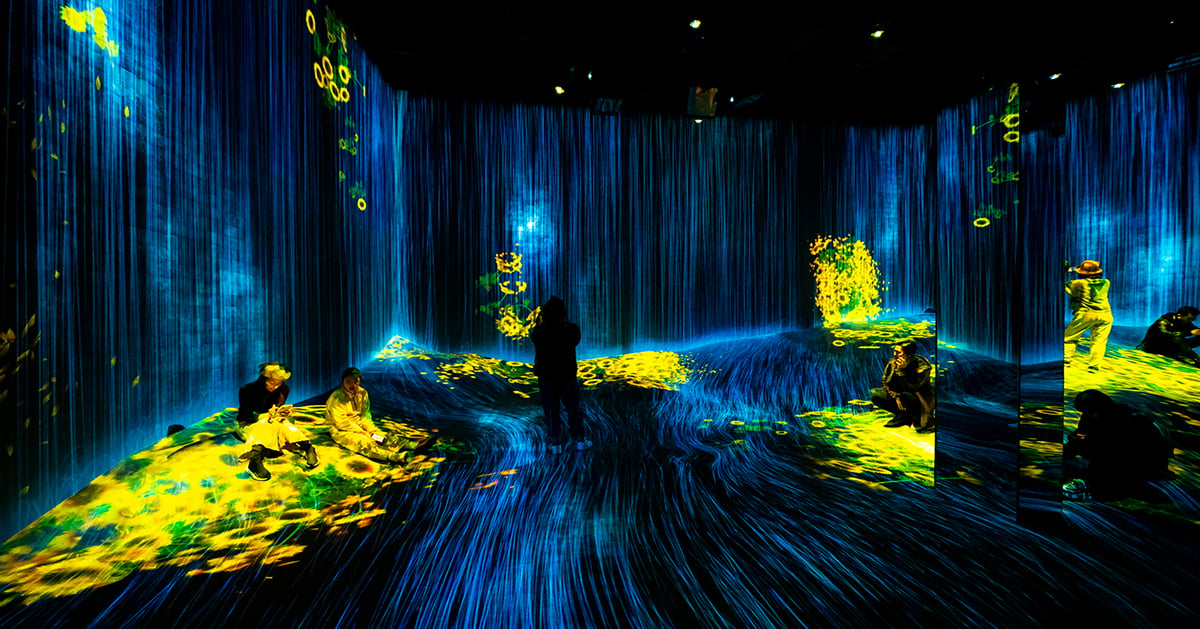
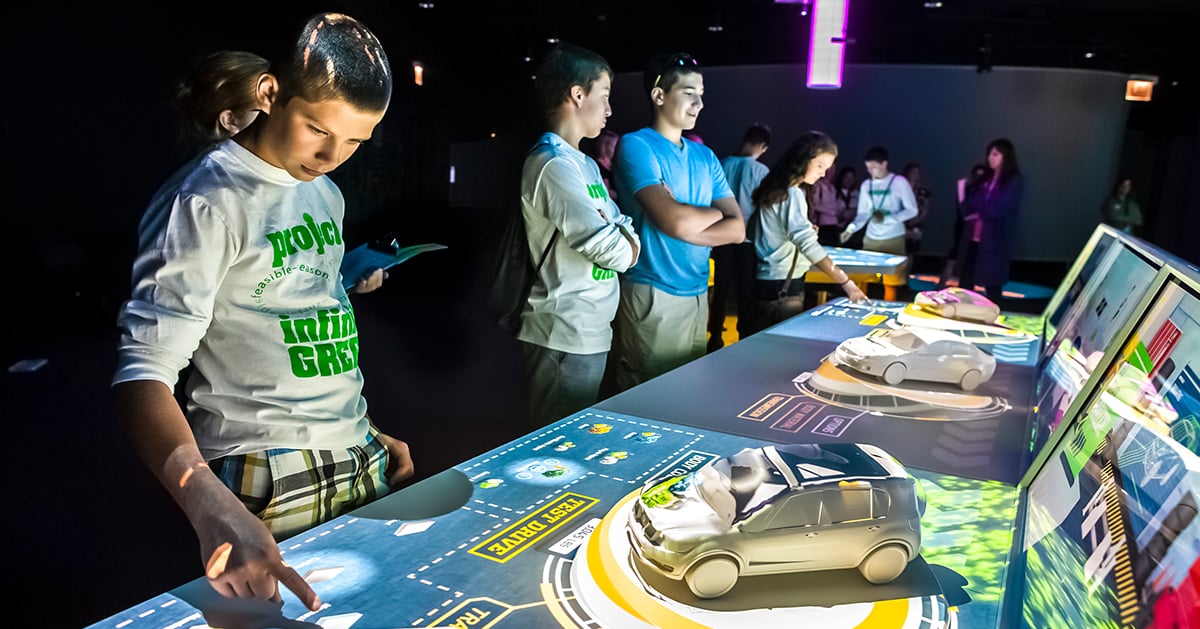
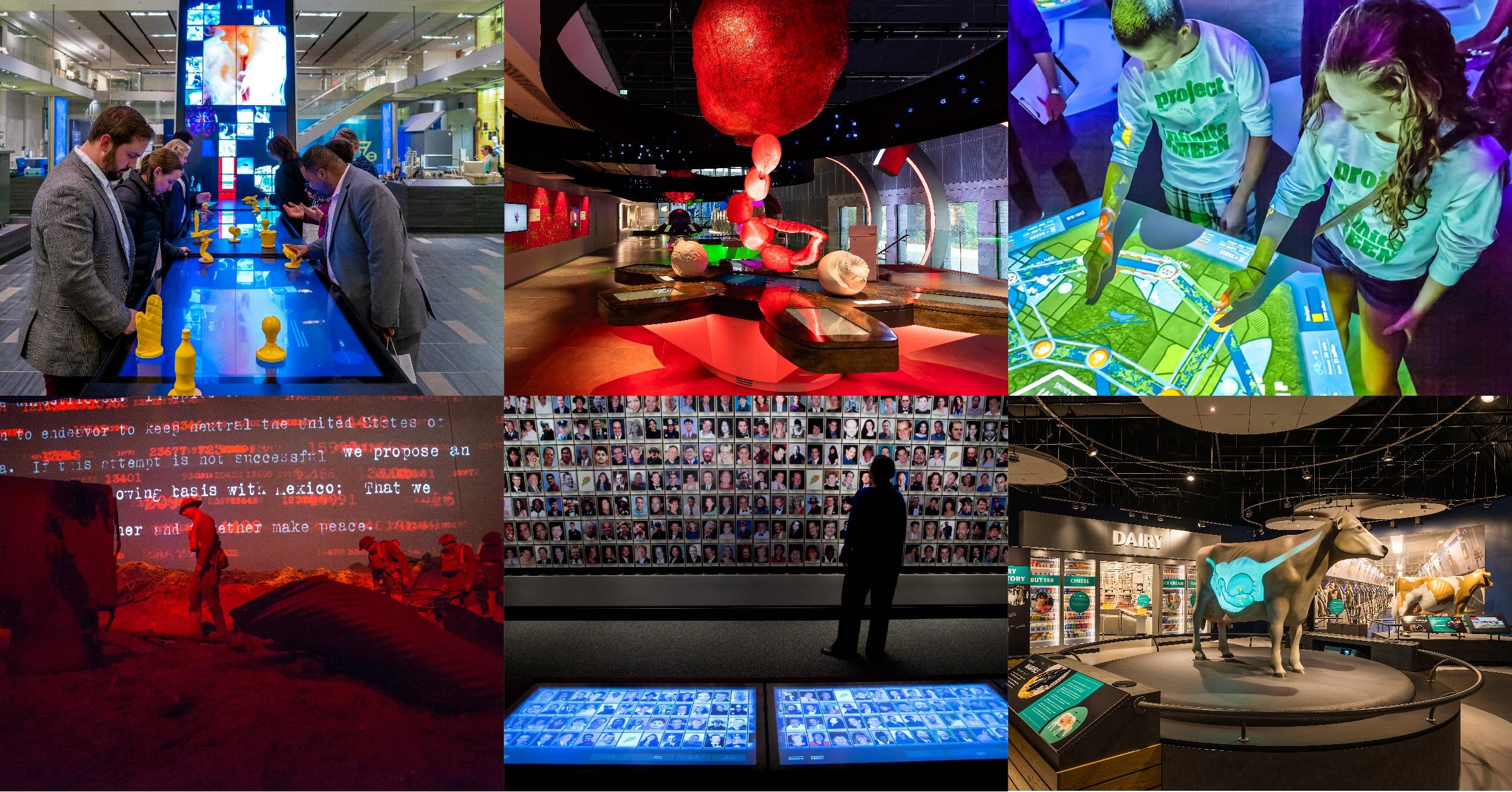
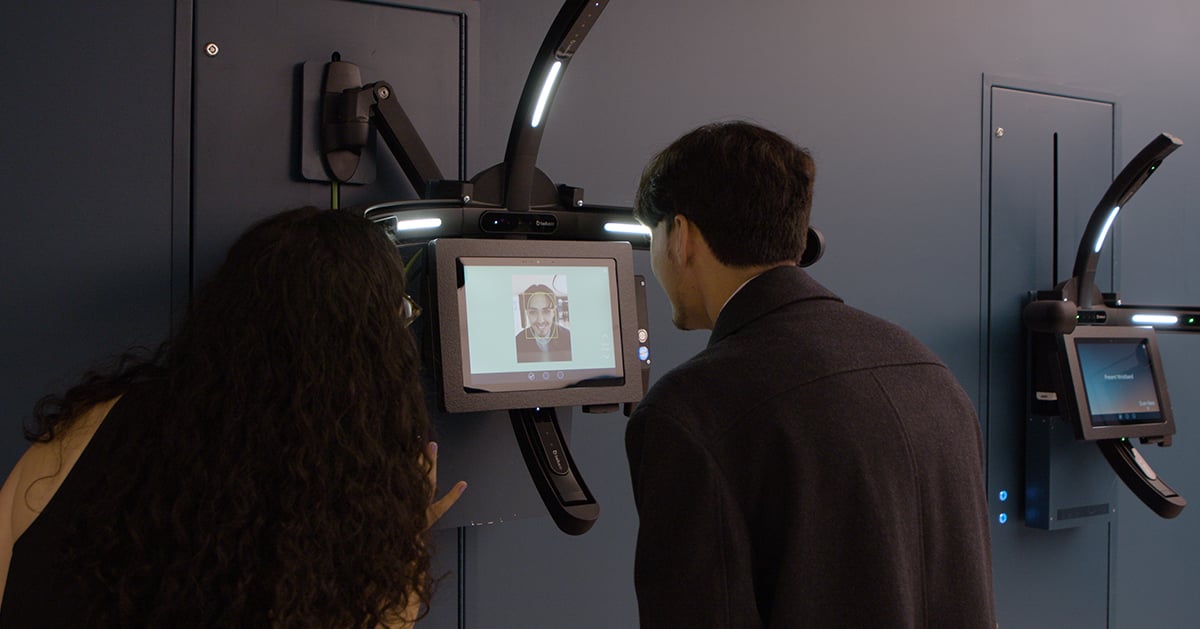
Johnson Controls' OpenBlue Innovation Center Milwaukee sets new standards for corporate briefing centers. An immersive, experiential space showcases the company's smart building technologies. The center demonstrates product benefits through innovative storytelling that features motion technologies, virtual reality, RFID technology and high levels of interactivity and personalization.
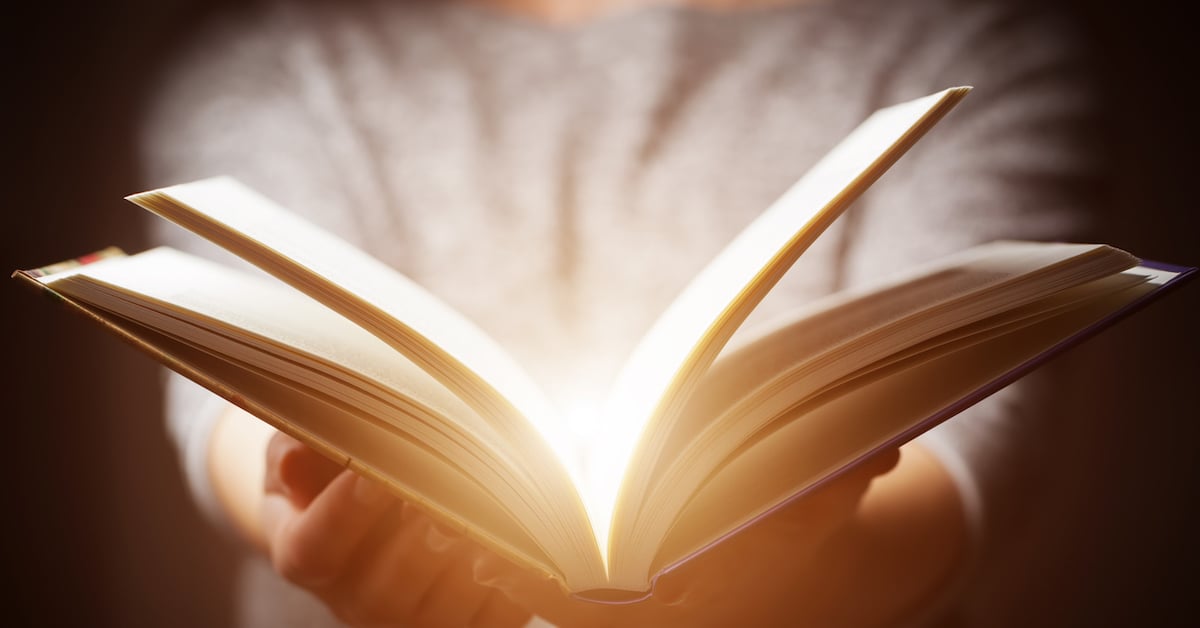
As visitors scroll through the pages of an interactive 'Projected Book,' they can explore individual products in a ground-breaking format that goes way beyond traditional touchscreens. The book interacts with animated projections utilizing advanced motion sensors and RFID technology embedded in the pages, enhancing engagement and providing an immersive learning experience.
A custom RFID tagging system and advanced motion sensors track readers' progress as visitors turn pages, animated images and text change dynamically. Content seamlessly blends literature, company history and technology into a visual narrative. The 'Book' educates visitors on the company's commitment to leadership in innovation and sustainability.
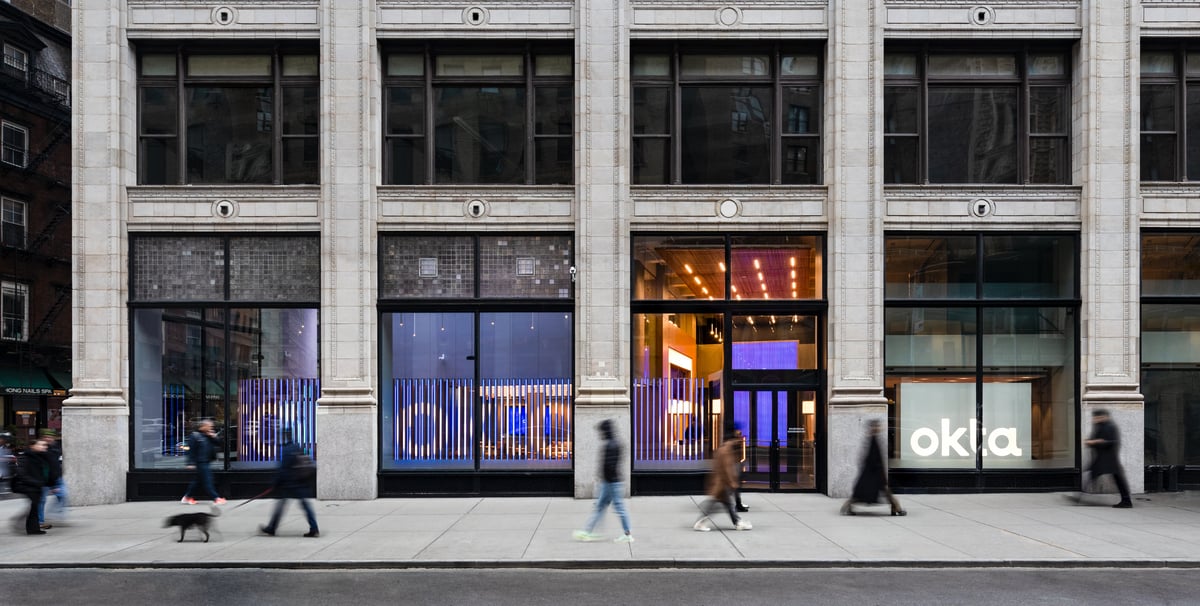
Okta Experience Center
The Okta New York Experience Center combines tracking and advanced motion sensing technology with real-time interactivity to tell a compelling story about the company's products inside and outside the building.
The building is in the heart of Manhattan on a busy corner of Broadway with high volumes of passing foot traffic. Large panoramic windows at the front of the building give passers-by a view into the interior lobby.
As visitors pass the windows, hidden LIDAR mapping tracks their movement. This triggers interaction with dynamic brand content, animations and visitors' own digital shadows. The content is displayed on a line of interactive LED 'fins' inside the window. This dynamic display of larger-than-life proportions captures attention and draws guests towards the center of the experience.
When visitors enter the experience center, they see two large dynamic 4K LED displays. They present key insights about OKTA and the importance of data security. Motion technologies sense visitor movement and proximity to trigger content on the displays. Speakers around the space create an immersive auditory experience to match the impressive visuals.
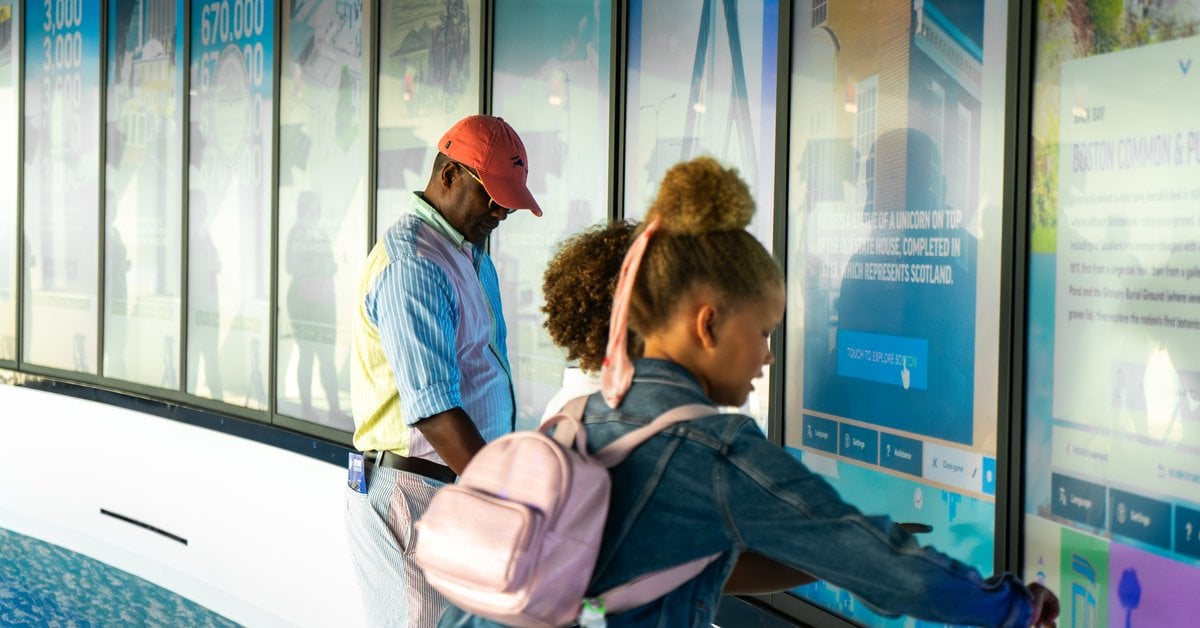
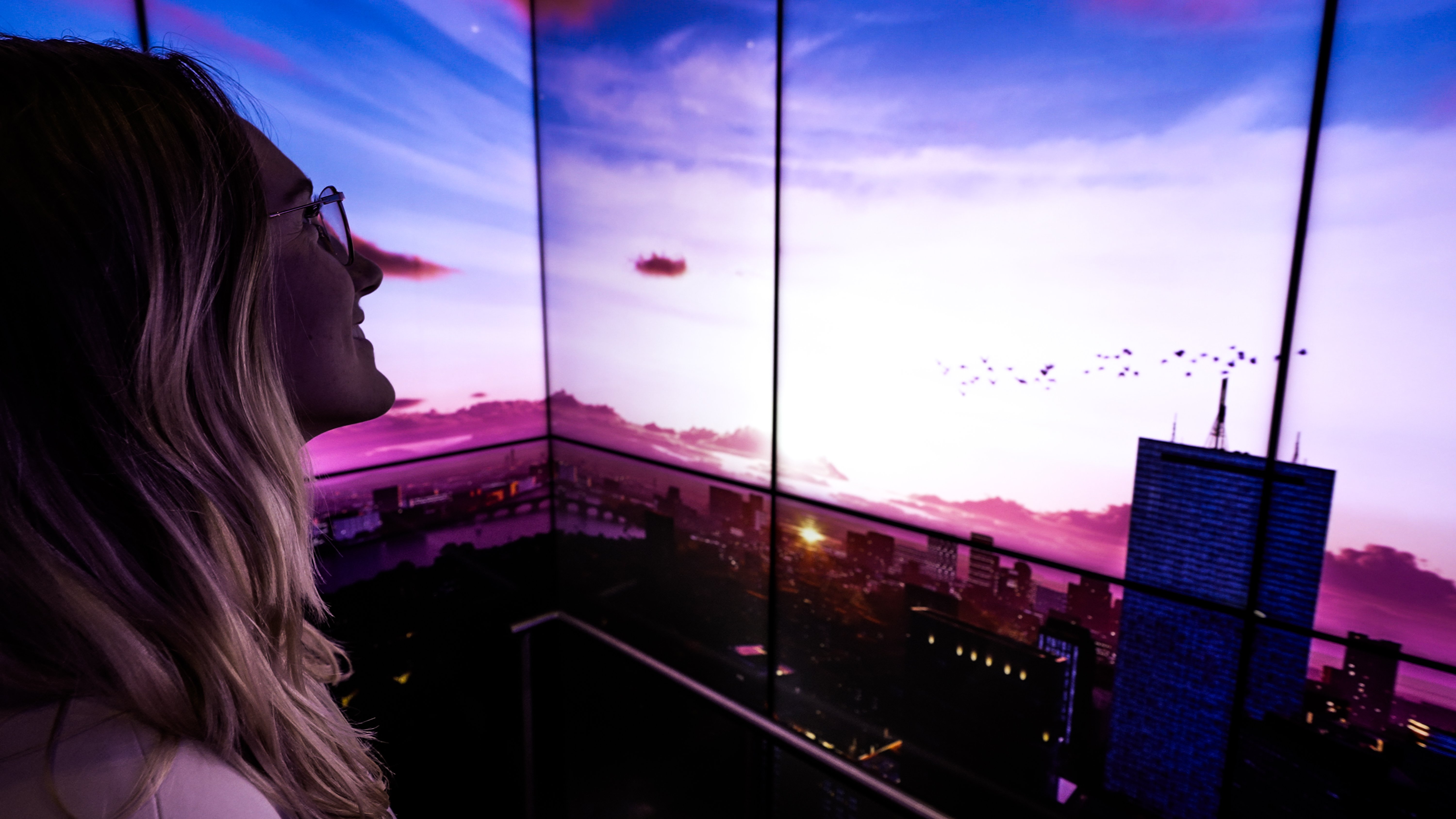
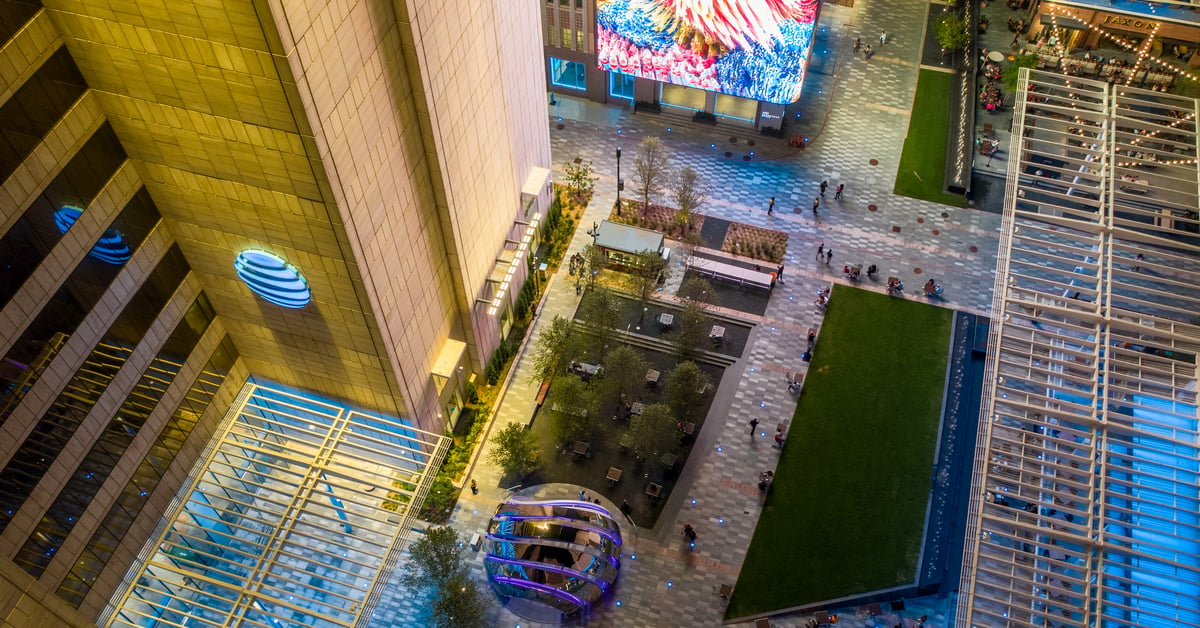
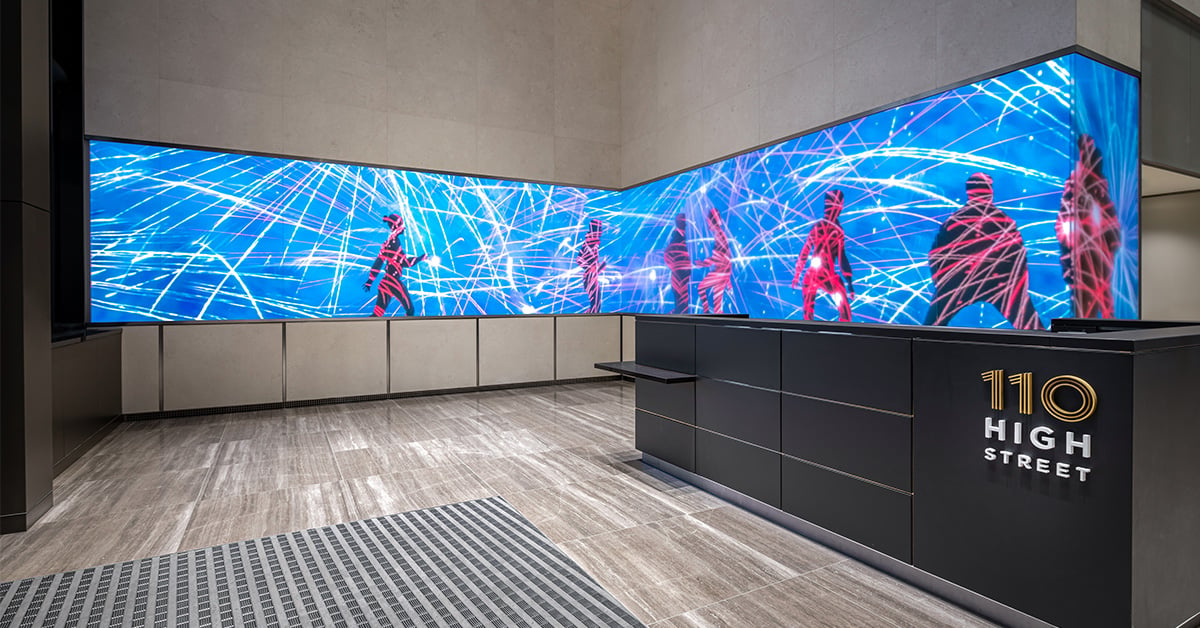
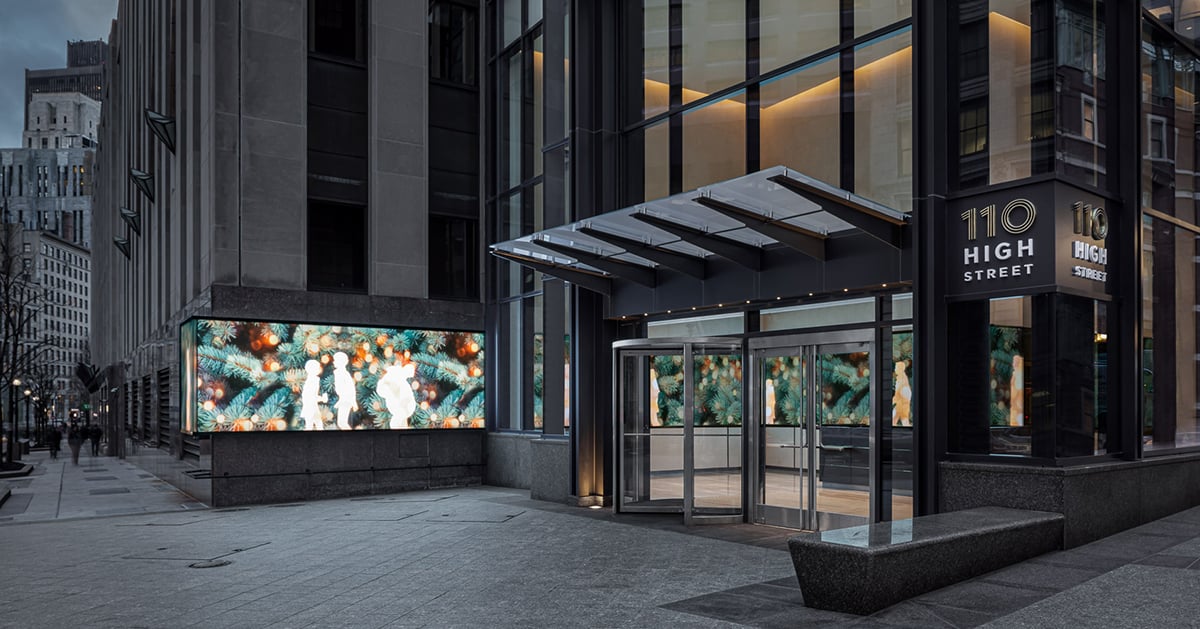
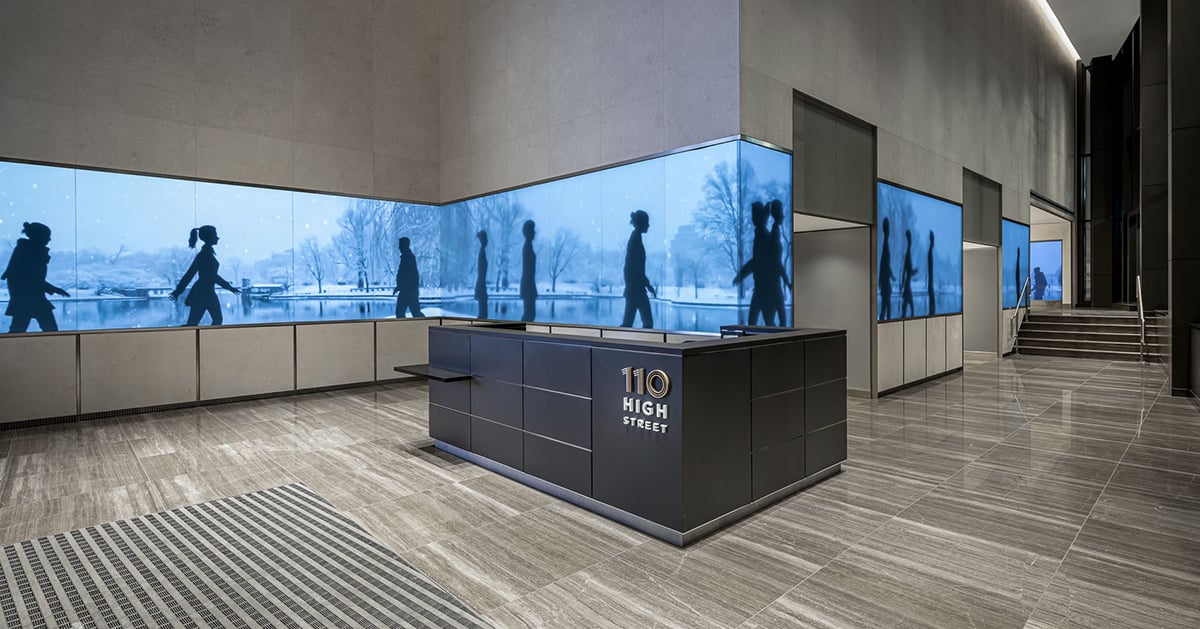
110 High Street, Boston
The owners of 110 High Street, Boston, wanted to create a dynamic, interactive experience. They aimed to demonstrate the building's energy and appeal and attract and retain high-profile tenants. The 100-foot digital Boston Digital Media Band incorporates advanced motion sensors that respond to people's presence with moments of surprise and delight.
Custom screens are seamlessly integrated into the architecture. They are programmed with media that provide different experiences for viewers at various distances. The LED wall offers a fun canvas for artists to create on. It's large enough to have an impact from outside the building but not so large that it dominates the lobby.
The media band is programmed with three digital art modes. The content reacts to passers-by or visitors in the lobby in various fun and interactive ways. Characters in Silhouette Mode wave and dance and wear weather-appropriate attire. They wear sports gear when the Boston Patriots, Red Sox, Bruins or Celtics play.
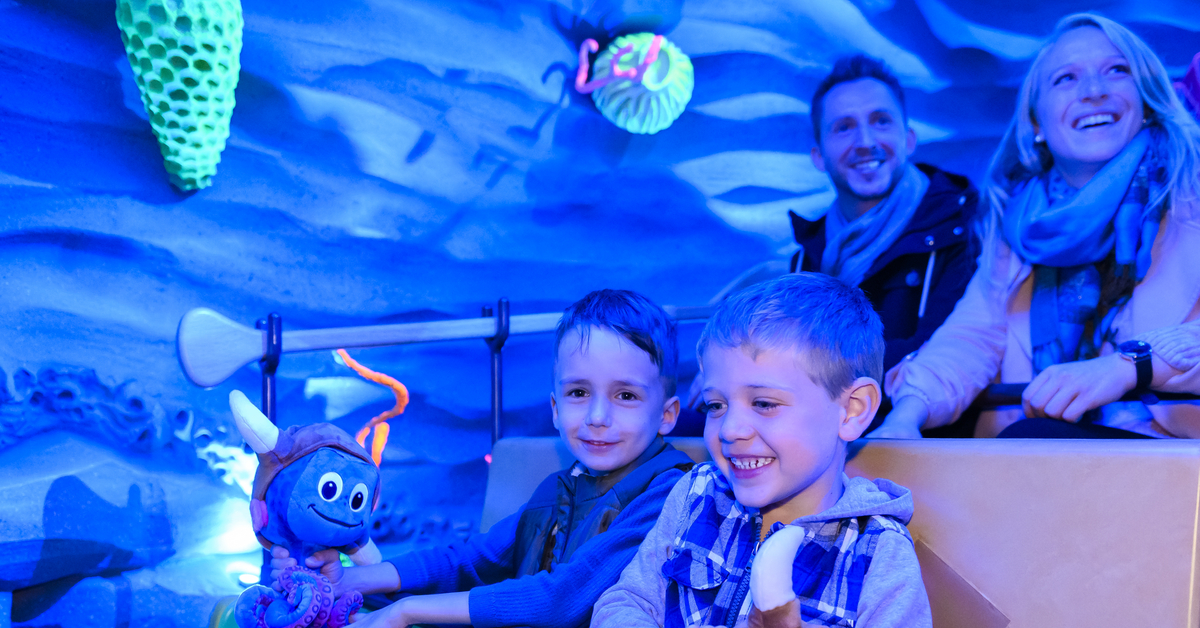
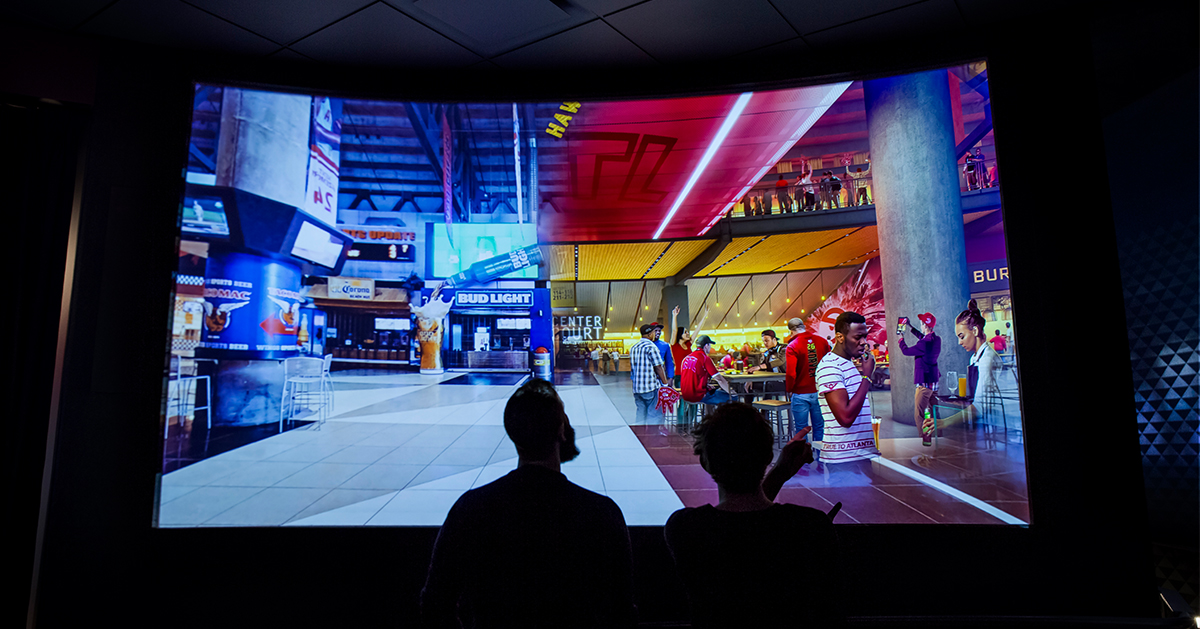
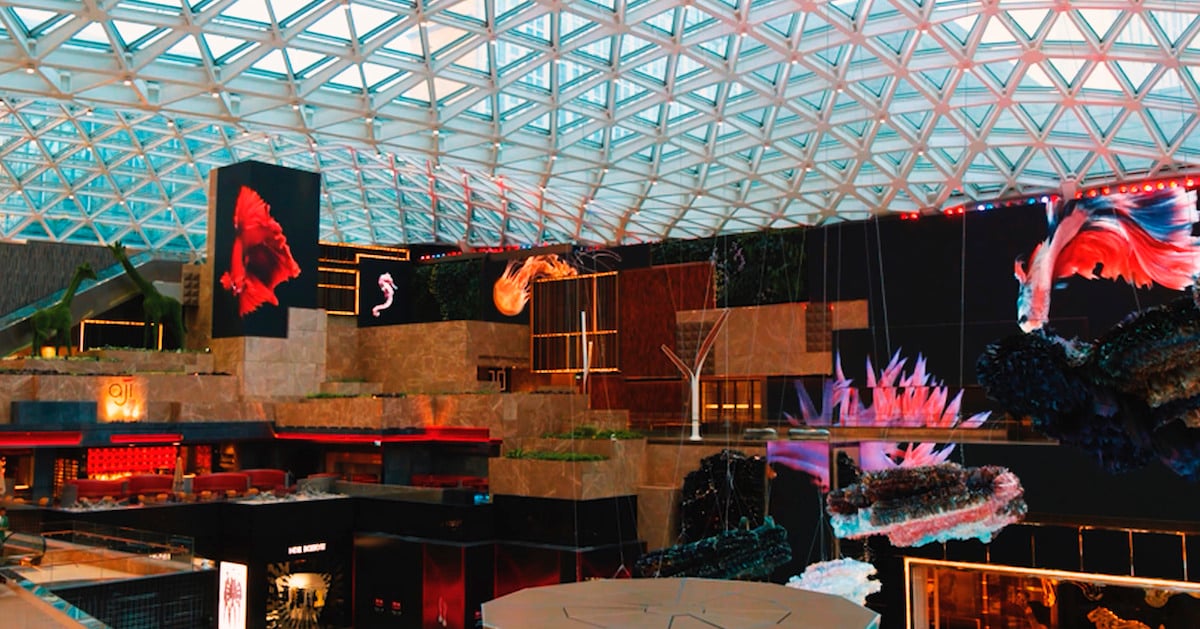
Orlando International Airport
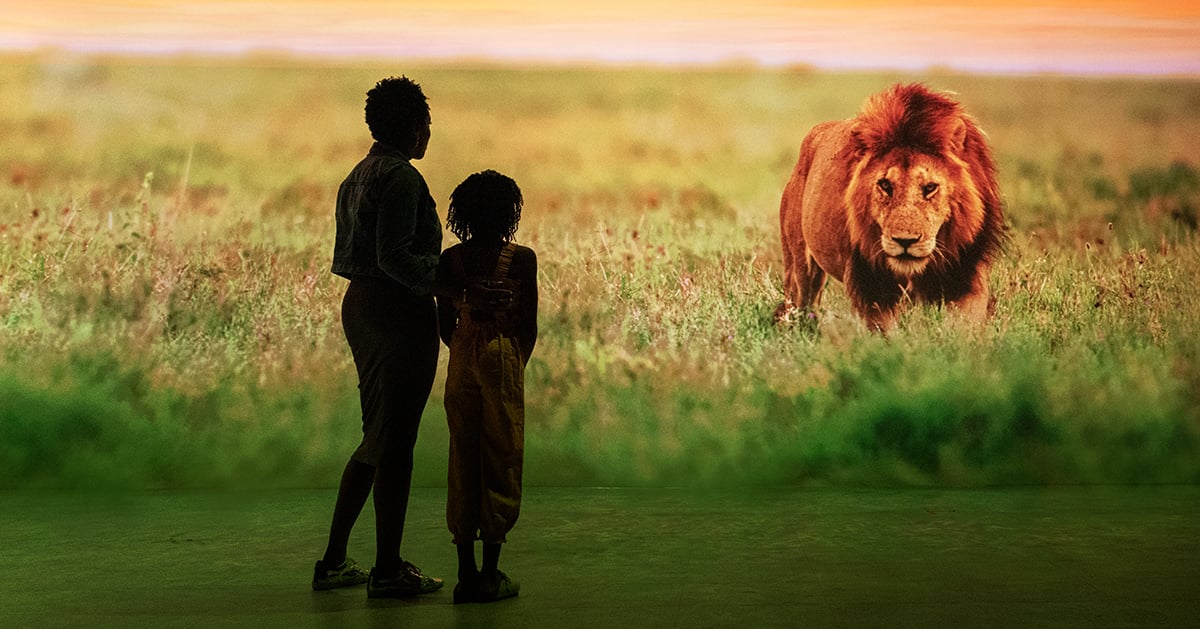
At Orlando International Airport, an installation known as the 'Moment Vault' transforms a busy, stressful day of traveling into a fun airport experience to remember.
LED screens mounted back-to-back in a circular shape create an immersive, interactive 360-degree space. In the interior space, motion capture powered by artificial intelligence integrates passenger silhouettes with dynamic content.
Multiple cameras track guests' movements inside the Moment vault. The motion capture system generates a 3-dimensional pose estimate for each guest. The system instantly converts a subject's motion into digital wireframes integrated into the real-time onscreen content. Guests see their virtual avatars displayed on the LED screens interacting with digital images, such as shoals of fish.
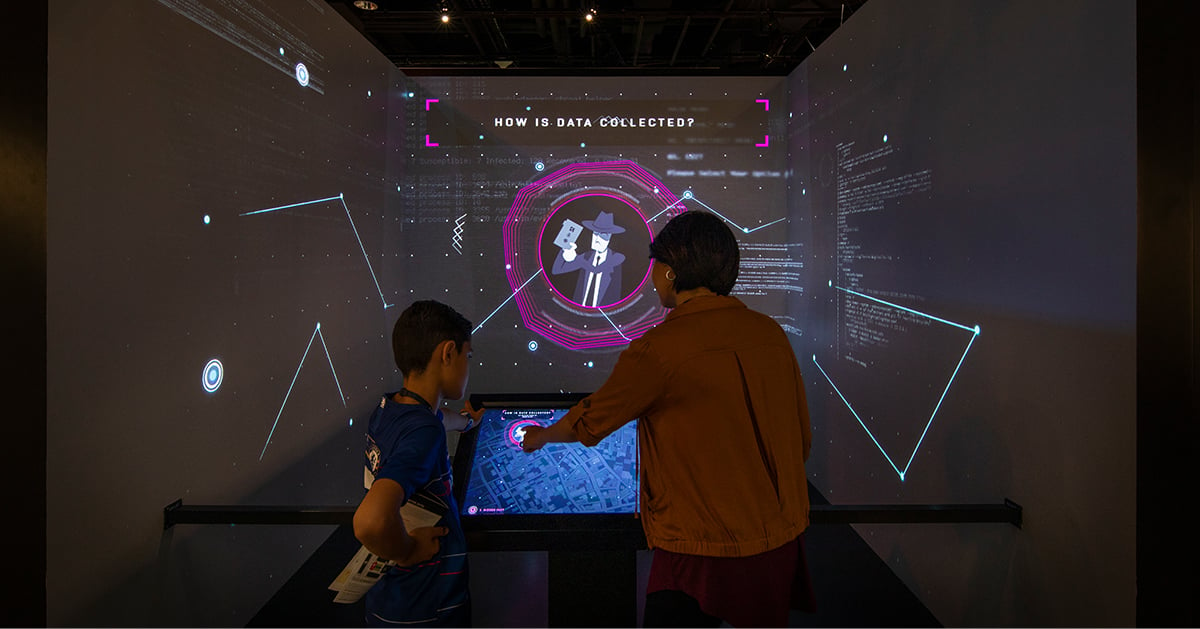
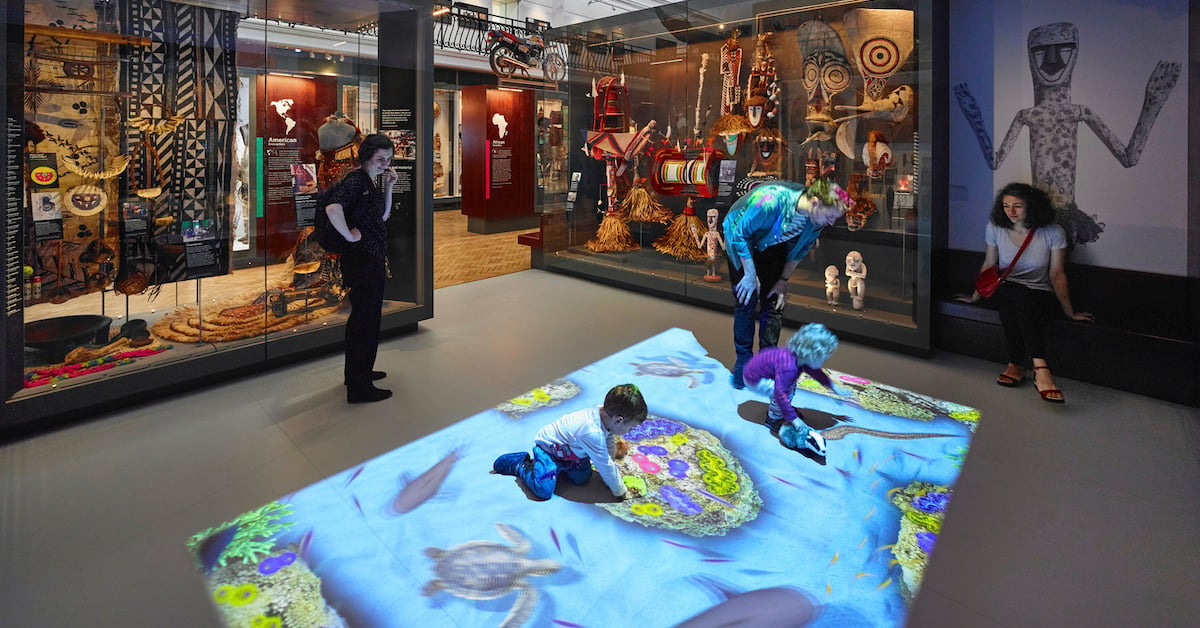
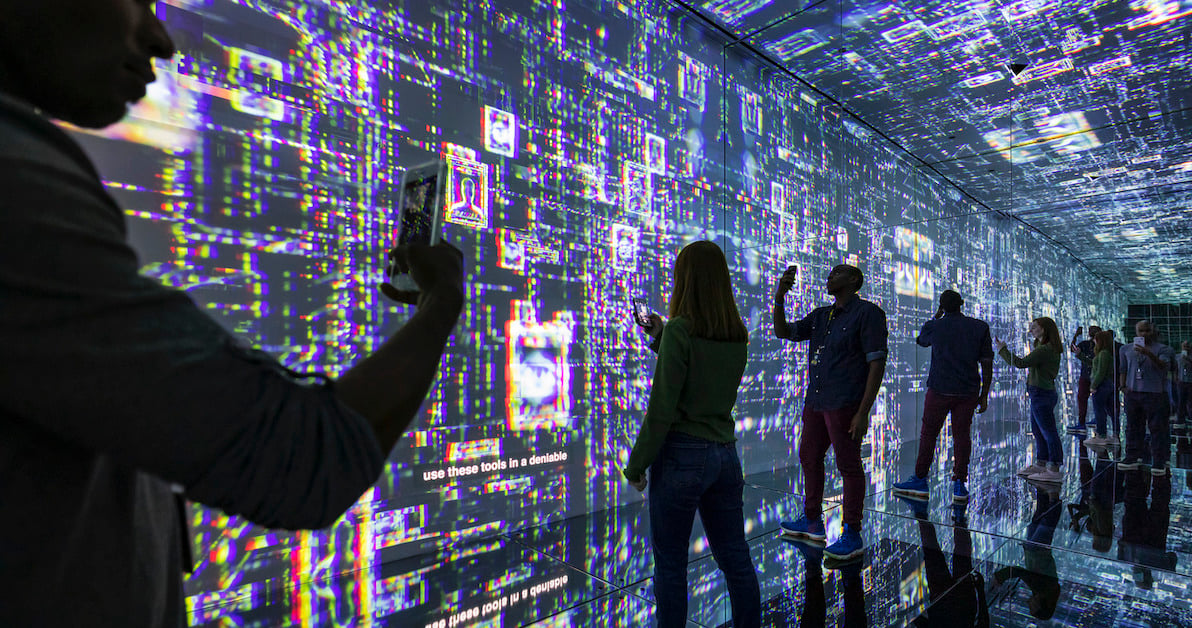
International Spy Museum
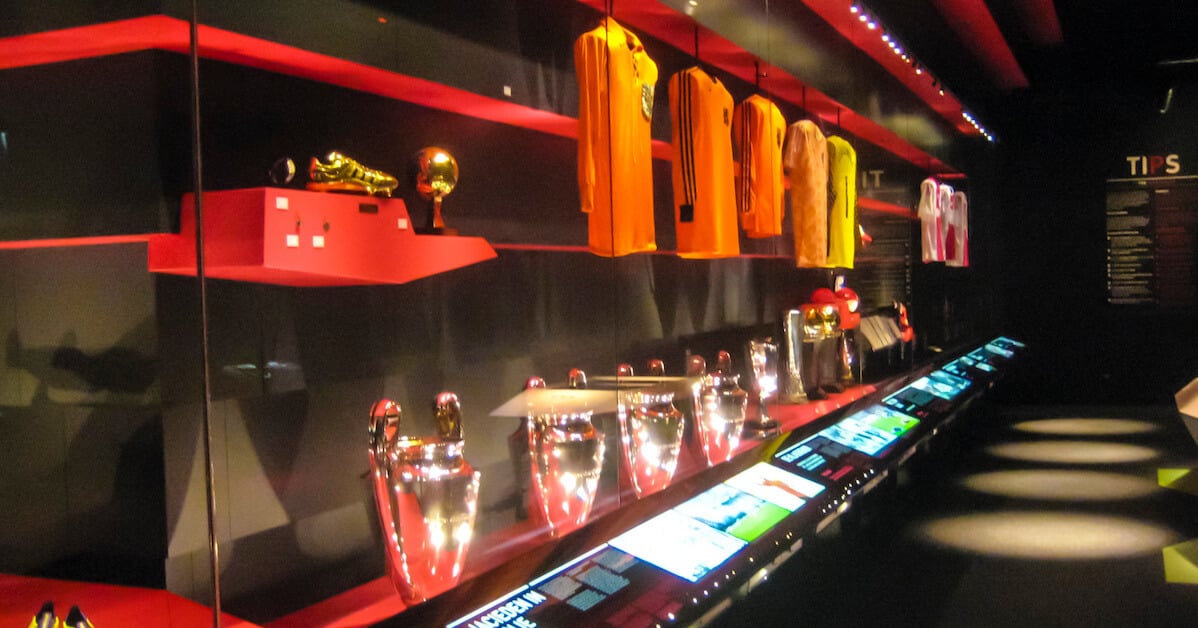
The International Spy Museum is part museum and part game. Interactive and immersive exhibits let visitors experience what it takes to be an officer, agent or analyst working in the shadows.
Visitors take on an 'Undercover Mission' by identifying themselves with a personalized interactive lanyard. They interact with displays that challenge them to complete demanding tasks. They must analyze clues, maintain cover, find and contact sources, collect intel at drop sites and complete other spy tasks.
The 'Sneaking into Berlin' challenge extensively uses hidden low-light cameras, advanced motion sensing and RFID technology. The exhibit detects and identifies individual visitors, demonstrating the power of surveillance. In one example, an image captured during the mission surprises visitors by appearing on another exhibit later in the mission.
These interactive motion technologies create a powerful, engaging and educational experience.
Sheikh Abdullah al Salem Cultural Centre
The Sheikh Abdullah al Salem Cultural Centre is the largest museum complex in the world. It covers 22,000 square meters and hosts four innovative museums - Natural History, Science Centre, Space and the Arabic Islamic Science Museum.
Interactive motion technologies in the Healthy Living gallery create a 'Race against the Stars' experience. Sixteen 80-inch LED screens mounted side-by-side create a virtual running track. Advanced motion sensor technology allows visitors to 'race' against the world's elite athletes. All entrants are accurately timed, and the fastest are posted on a daily leader board to encourage participation, healthy competition and excitement.
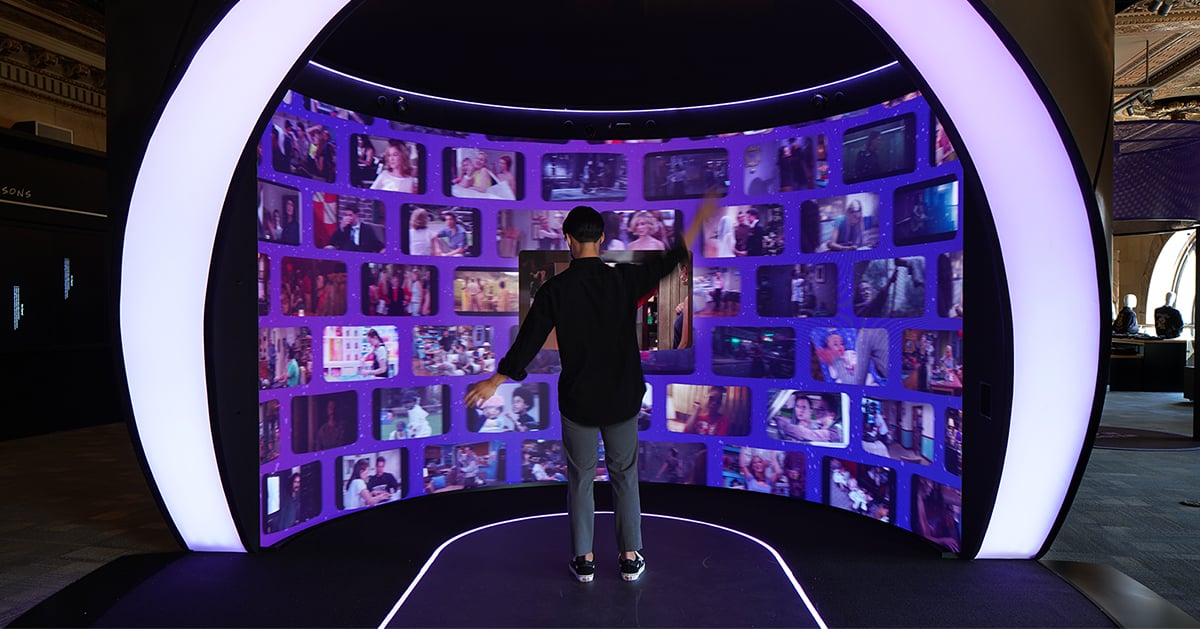
The Orbit
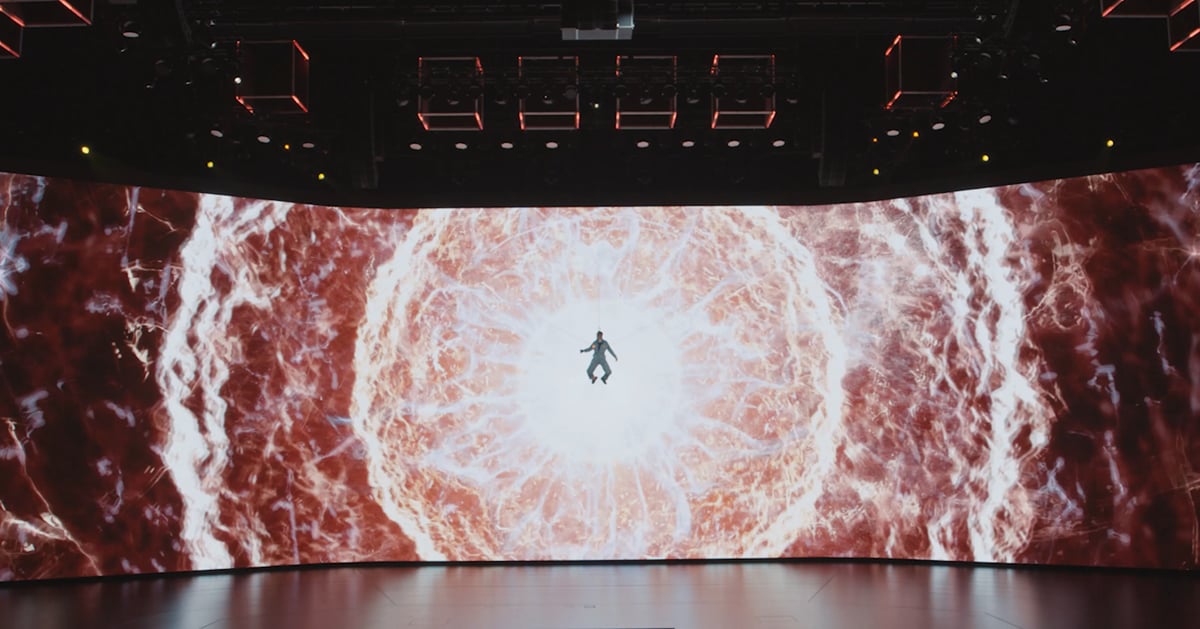
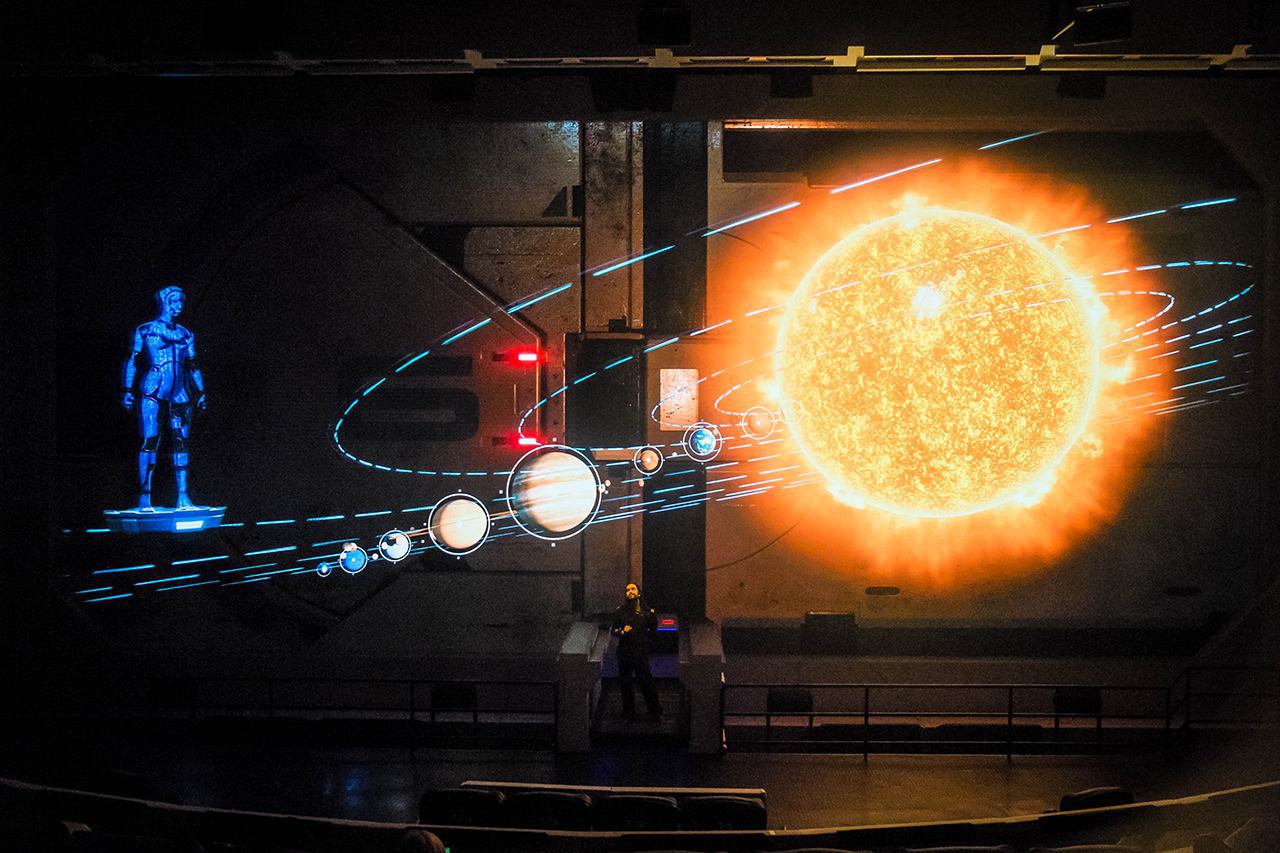
The Orbit is an interactive experience that promotes and showcases HBO Max's brands. The 360° interactive experience allows visitors to interact with iconic moments, characters and stories in a personalized, intuitive way.
Using machine learning, advanced motion sensing technology and voice recognition, the experience tracks how a user moves their face or arms. It then displays clips of HBO Max characters matching their movements in real-time.
The Orbit sets new standards in guest experience, enabling visitors and customers to experience content from HBO Max in ways they had never seen before. The Orbit creates an innovative retail experience that blurs the boundaries between retail and entertainment.
Designing interactive experiences with motion technologies
The concept of a motion-based guest experience is relatively simple. A visitor enters a space or gestures. Advanced motion sensors capture or track the movement. The system gathers data and triggers a response or supports interaction with content or audio.
However, as the examples show, these interactive experiences require skilled design, advanced motion technologies and complex integration to bring the designer's vision to life.
To develop the most appropriate technology solution, technology system designers collaborate with an ecosystem, of experience designers, content creators and technology partners. One of the most important decisions is selecting suitable sensors and the optimum motion technologies.
Advanced motion sensors are used in different types of sensing devices, including:
- Cameras (depth-sensing, RGB, IR)
- Mobile devices
- Wearables
- Touchscreens
- Overlays
- Proximity sensors
- Occupancy/vacancy sensors
The main types of Motion technologies include:
- Passive Infrared (PIR): These sensors detect changes in infrared radiation emitted by objects in their field of view. They are commonly used in interactive experiences, security systems, automatic lighting and occupancy detection.
- Ultrasonic: Ultrasonic sensors emit high-frequency sound waves and measure the time it takes for the waves to bounce back after hitting an object. They are used in motion detection, object detection and distance measurement applications.
- Microwave: Microwave sensors emit microwave pulses and analyze the reflections to detect motion. They are often used in automatic door openers, traffic flow monitoring and industrial automation.
- Laser: Laser sensors emit laser beams and detect changes in the reflected light to measure distance or detect motion. They are used in applications such as robotics, navigation and industrial automation.
- Computer Vision: Computer vision uses an image from a camera and machine learning to identify objects and their movements.
- Global Positioning System (GPS): GPS uses four-dimensional positioning from satellites to track movement on a large scale.
Some sensors combine two or more technologies, such as PIR and microwave, to improve accuracy and reduce false alarms.
Increasingly, interactive experience designers are integrating motion technologies with related systems, such as building management, access control, surveillance or environmental management systems. This allows designers to use existing infrastructure and create a holistic solution for optimizing guest experience.
Designers are also taking advantage of the latest advanced motion technologies to improve performance.
- Wireless mesh sensors: Wireless mesh sensors communicate with the nearest compatible device, enabling easy installation and flexible configuration.
- IoT-enabled sensors: IoT-enabled motion sensors connect to the network, allowing for remote monitoring, control and data analytics.
- Advanced analytics: Motion sensors with advanced analytics capabilities enable more sophisticated crowd detection, occupancy tracking and behavioral analysis.
- Machine learning and AI: Emerging technologies leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence to analyze motion data and identify patterns, anomalies and security threats.
Benefits of interactive motion technologies for guest experience
Motion technologies provide owners and operators with many essential benefits.
- The technologies enhance guest experience, helping to attract and retain more visitors. In paid venues, this helps increase revenue and profitability.
- Data from advanced sensor technologies provides valuable insights into guest behavior and response to interactive experiences.
- Interactive motion technologies improve accessibility, helping attract a more diverse audience.
- Insights from advanced motion sensors help optimize space usage by identifying the most popular attractions.
- Data on usage and attendance can be used to identify opportunities to reduce energy usage and improve operational efficiency.
Working with specialists in motion technologies
To optimize the guest experience, it's essential to work with a partner who has an in-depth understanding of all aspects of interactive motion technologies.
With 60 years' experience in themed and location-based entertainment, Electrosonic provides a comprehensive end-to-end design, build and support service for guest experiences featuring interactive motion technologies.
We have access to the latest advanced motion technologies through our Technology Partner Program and collaborate with trusted partners in content development, control systems, experience design and fabrication.
Ryan Poe
Ryan Poe, Electrosonic’s Director of Technology Solutions, works and writes on the frontiers of advanced technology. He is a trusted adviser on leveraging technology in new ways and works within our Innovation Garage framework to evaluate new technologies and develop resources that support a portfolio of advanced services.










.jpg?width=1500&height=995&name=ELC501_N17_medium%20(1).jpg)

![[Amaze and captivate with Projection Technology]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/5104351/9de9e463-6447-4a55-aaac-40b3e241fd60.png)

.jpg?width=1200&height=628&name=OKTA_N5_cropped_1200x628%20(1).jpg)
![Discover Digital Placemaking [eBook]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/5104351/ff4c7c00-827c-4d0a-aa90-2cf65d07d403.png)

.jpg?width=1200&height=628&name=MCO1_N21_cropped_1200x628%20(1).jpg)